You are project manager of HHK project. Examine the network diagram given below: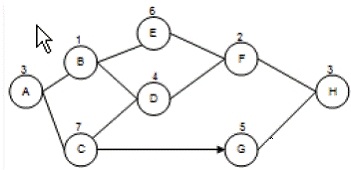
A vendor reports that he will be four days late on the materials you’ll need in order to complete
Activity E. Based on the project network diagram, how many days can Activity E be delayed?

A.
Four days
Activity Name
B.
Six days
Activity ID
C.
Five days
Risk event
D.
Zero, it is on the critical path.
WBS ID
E.
QUESTION 233
Paula works as a project manager for her organization. She is working with the project team to
define the activity attributes. Which of the following is NOT a valid activity attribute?
A.
Four days
Activity Name
B.
Six days
Activity ID
C.
Five days
Risk event
D.
Zero, it is on the critical path.
WBS ID
Explanation:
Activity E has four days of float. The entire project will take 19 days to complete. Float, also called
slack, is the amount of time an activity can be delayed without affecting any subsequent activities.
There are two types of floats available: Free Float: It is the amount of time a schedule activity can
be delayed without delaying the early start date of any immediately following schedule activities.
Total Float: It is the total amount of time that a schedule activity may be delayed from its early startdate without delaying the project finish date, or violating schedule constraint. Float is calculated by
using the critical path method technique.
Answer option D is incorrect. Activity E is not on the critical path.
Answer options C and B are incorrect. These are incorrect calculations of the amount float
available for ActivityRisk events are not associated with the activity attributes, but are recorded in the project risk
register. Risk events are the distinct and particular occurrence that negatively affects a decision or
a plan. Activity attributes are an output of the Define Activity process. These attributes refer to the
multiple components that frame up an activity. The components for each activity during the early
stages of the project are the Activity ID, WBS ID, and Activity name. At the later stages, the activity
attributes include Activity codes, Predecessor activity, activity description, logical relationship,
successor activity, leads and lags, imposed dates, and constraints and assumptions. Activity
attributes are used for schedule development and for ordering, selecting, and sorting the planned
schedule activities in a number of ways within reports.

