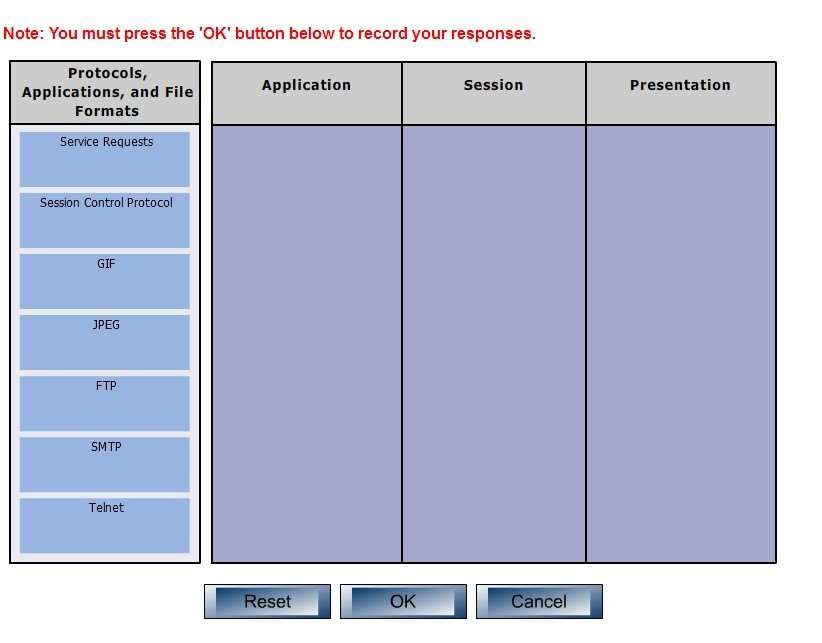
DRAG DROP
Click and drag the following protocols, applications, and file formats on the left, to their corresponding Open
Systems Interconnection (OSI) layers.
Select and Place:

Explanation:
The application layer is responsible for interacting directly with the application. It provides application services
such as e-mail and File Transfer Protocol (FTP), Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) and telnet. Some of its
associated protocols include:
FTP: Used to transfer data between hosts through the Internet or a network.
SMTP: SMTP is a Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)/Internet Protocol (IP) protocol which is used to send
and receive e-mail messages.
Telnet: Used to allow remote logins.
The session layer is used to create, manage, and terminate sessions between communicating nodes. Some of
the protocols and applications associated with this layer include:Service requests: Service requests and service responses which take place between different applications
are handled by the session layer.
Session Control Protocol (SCP): Allows a host to have multiple conversations with another host using the
same TCP connection.
The Presentation layer in the OSI model enables coding and conversion functions for application layer data.
The formatting and encryption of data is done at this layer, as the Presentation layer converts data into a format
which is acceptable by the application layer. Some of the file types associated with this layer include:
Graphics Interchange Format (GIF)
Joint Photographic Experts Group (JPEG)
Tagged Image File Format (TIFF)
Other layers in the OSI model include:
Transport: Responsible for error free and sequential delivery of data. This layer is used to manage data
transmission between devices, a process known as flow control. The Transport layer protocols are
Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and User Datagram Protocol (UDP).
Physical: Consists of hardware for sending and receiving data on a carrier. The protocols which work at the
Physical layer include Fast Ethernet, RS232, and Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM).
Network: Used to define the network address or the Internet Protocol (IP) address which is then used by the
routers to forward make forwarding decisions.
Data Link: Ensures reliable transmission of data across a network on the basis of Layer 2 addresses such
as MAC addresses (Ethernet) or DLCIs (Frame Relay).
Objective:
Network Fundamentals
Sub-Objective:
Compare and contrast TCP and UDP protocolsCisco Documentation > Internetworking Technology Handbook > Internetworking Basics > OSI Model and
Communication Between Systems