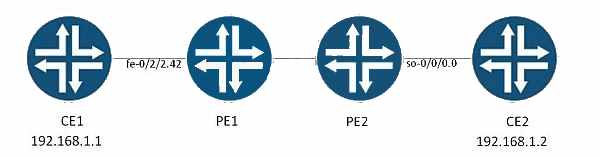
— Exhibit —
Refer to the Exhibit.
Referring to the exhibit, you see the proper BGP, MPLS, and routing instance configuration for
PE1 and PE2.
Which configuration on PE1 will allow CE1 to communicate with CE2 over a Layer 2 VPN,
assuming PE2 has PPP TCC encapsulation on so-0/0/0.0?

A.
[edit interfaces fe-0/2/2 unit 42]
family tcc {
proxy {
inet-address 192.168.1.2;
}
remote {
inet-address 192.168.1.1;
}
}
B.
[edit interfaces fe-0/2/2 unit 42]
family tcc {
remote {
inet-address 192.168.1.2;
}
}
C.
[edit interfaces fe-0/2/2 unit 42]
family tcc {
proxy {
inet-address 192.168.1.1;
}
}
D.
[edit interfaces fe-0/2/2 unit 42]
family tcc {
proxy {
inet-address 192.168.1.1;
}
remote {
inet-address 192.168.1.2;
}
}


hi, is it valid this dump?
0
0
yups 100% valid till today……just done 7th march
0
0
Answer – A.
Configuring Ethernet Encapsulation for Layer 2 Switching TCCs
For Ethernet TCC circuits, configuring the encapsulation type for the entire physical device by specifying the value ethernet-tcc for the encapsulation statement.
You must also specify static values for a remote address and a proxy address at the [edit interfaces interface-name unit unit-number family tcc] or [edit logical-systems logical-system-name interfaces interface-name unit unit-number family tcc] hierarchy level.
The remote address is associated with the TCC switching router’s Ethernet neighbor; in the remote statement you must specify both the IP address and the media access control (MAC) address of the Ethernet neighbor. The proxy address is associated with the TCC router’s other neighbor connected by the unlike link; in the proxy statement you must specify the IP address of the non-Ethernet neighbor.
You can configure Ethernet TCC encapsulation for the interfaces on 1-port Gigabit Ethernet, 2-port Gigabit Ethernet, 4-port Fast Ethernet, and 4-port Gigabit Ethernet PICs.
encapsulation ethernet-tcc;
unit logical-unit-number {
family tcc {
proxy {
inet-address ip-address;
}
remote {
inet-address ip-address;
mac-address mac-address;
}
}
}
0
0
Does anyone knows if this is a valid dump?
0
0
this dump is valid 100% , 20 feb 2015 ,JNCIP JN0-660 , Good Luck all
0
0
100% valid dumps……done just today……..
0
0
http://www.juniper.net/techpubs/en_US/junos13.1/topics/task/configuration/tcc-layer-two-five-circuits-interface-encapsulation-solutions.html
0
0
100% valid dump. just passed.
thank you to the friend for posting it. good luck to all.
0
0
http://www.juniper.net/techpubs/en_US/junos14.1/topics/usage-guidelines/interfaces-configuring-vlan-tcc-encapsulation.html
The proxy address is the IP address of the non-Ethernet TCC neighbor for which the TCC router is acting as a proxy. ==> CE2 here
The remote address is the IP or MAC address of the remote router. The remote statement provides ARP capability from the TCC switching router to the Ethernet neighbor. The MAC address is the physical Layer 2 address of the Ethernet neighbor
So A is correct
0
0
is this dump still valid??
0
0
Hi
It is stil valid.
I successfully cleared the exam today June 26th 2015.
passing score 97%
0
0
Is this dump still valid? I will take the exam by the end of July.
0
0
Hi
It is still valid.
I successfully cleared the exam.
passing score 90%
0
0
plz confirm the dumps is still valid???
0
0
100% confirmed dumps…….
0
0
100% Valid dump just passed today 86%
0
0
guys are these enough to get through the exam?
0
0
Are these still valid?
0
0
pretty OK, still valid.
0
0
still a valid dump ?
0
0
Is passing score for JNCIP-SP is 65% same like JNCIS-SP or it’s different?
0
0
100% valid till today
0
0
still a valid dump ?
0
0