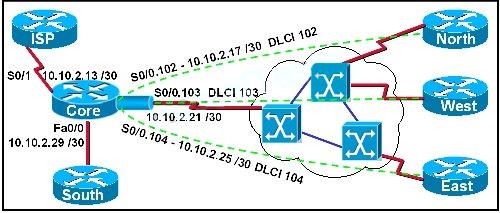
Refer to the exhibit.
The network associate is configuring OSPF on the Core router. All the connections to the
branches should be participating in OSPF. The link to the ISP should NOT participate in OSPF
and should only be advertised as the default route. What set of commands will properly configure
the Core router?

A.
Core(config-router)# default-information originate
Core(config-router)# network 10.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 0
Core(config-router)# exit
Core(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.10.2.14
B.
Core(config-router)# default-information originate
Core(config-router)# network 10.10.2.13 0.0.0.242 area 0
Core(config-router)# exit
Core(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.10.2.14
C.
Core(config-router)# default-information originate
Core(config-router)# network 10.10.2.16 0.0.0.15 area 0
Core(config-router)# exit
Core(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.10.2.14
D.
Core(config-router)# default-information originate
Core(config-router)# network 10.10.2.32 0.0.0.31 area 0
Core(config-router)# exit
Core(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.10.2.14


There are two ways to inject a default route into a normal area.
1. If the ASBR already has the default route in its routing table, you can advertise the existing 0.0.0.0/0 into the OSPF domain with the default-information originate router configuration command.
2. If the ASBR doesn’t have a default route, you can add the keyword always to the default-information originate command (default-information originate always). This command will advertise a default route into the OSPF domain, regardless of whether it has a route to 0.0.0.0.
Another benefit of adding always keyword is that it can add stability to the internetwork.
For example, if the ASBR is learning a default route from another routing domain such as RIP and this route is flapping, then without the always keyword, each time the route flaps, the ASBR will send a new Type 5 LSA into the OSPF domain causing some instability inside the OSPF domain. With the always keyword, the ASBR will advertise the default inside the OSPF domain always, and thus the flapping of the default route from the RIP domain will not cause any instability inside the OSPF domain.
In the example shown here, only choice D is correct as the wildcard mask correctly specifies the 10.10.2.16 0.0.0.15 networks, which include all IP addresses in the 10.10.2.16-10.10.2.31 range. In this question we were told that the ISP link should NOT be configured for OSPF, making choice A incorrect.
Autonomous system boundary router (ASBR) An autonomous system boundary router is a router that is connected by using more than one routing protocol and that exchanges routing information with routers autonomous systems. ASBRs typically also run an exterior routing protocol (e.g., BGP), or use static routes, or both.
0
0
16 – 15
0
0
lowest subnet
0
0