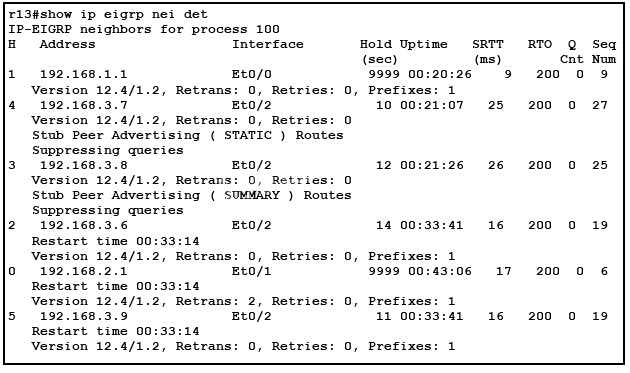
Refer to the exhibit.
After a link flap in the network, which two EIGRP neighbors will not be queried for alternative
paths? (Choose two.)

A.
192.168.1.1
B.
192.168.3.7
C.
192.168.3.8
D.
192.168.3.6
E.
192.168.2.1
F.
192.168.3.9
Explanation:
Both 192.168.3.7 & 192.168.3.8 are in an EIGRP Stub area
The Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) Stub Routing feature improves network
stability, reduces resource utilization, and simplifies stub router configuration.
Stub routing is commonly used in a hub and spoke network topology. In a hub and spoke network,
one or more end (stub) networks are connected to a remote router (the spoke) that is connected to
one or more distribution routers (the hub). The remote router is adjacent only to one or more
distribution routers. The only route for IP traffic to follow into the remote router is through a
distribution router. This type of configuration is commonly used in WAN topologies where the
distribution router is directly connected to a WAN. The distribution router can be connected to
many more remote routers. Often, the distribution router will be connected to 100 or more remote
routers. In a hub and spoke topology, the remote router must forward all nonlocal traffic to a
distribution router, so it becomes unnecessary for the remote router to hold a complete routing
table. Generally, the distribution router need not send anything more than a default route to the
remote router.
When using the EIGRP Stub Routing feature, you need to configure the distribution and remote
routers to use EIGRP, and to configure only the remote router as a stub. Only specified routes are
propagated from the remote (stub) router. The router responds to queries for summaries,
connected routes, redistributed static routes, external routes, and internal routes with the message
“inaccessible.” A router that is configured as a stub will send a special peer information packet to
all neighboring routers to report its status as a stub router. Any neighbor that receives a packet
informing it of the stub status will not query the stub router for any routes, and a router that has a
stub peer will not query that peer. The stub router will depend on the distribution router to send the
proper updates to all peers.http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/12_0s/feature/guide/eigrpstb.html#wp1021949