Your network consists of a single Active Directory domain. All domain controllers run
Windows Server 2008 R2. The Audit account management policy setting and Audit directory
services access setting are enabled for the entire domain.
You need to ensure that changes made to Active Directory objects can be logged. The
logged changes must include the old and new values of any attributes.
What should you do?

A.
Run auditpol.exe and then configure the Security settings of the Domain Controllers OU.
B.
From the Default Domain Controllers policy, enable the Audit directory service access
setting and enable directory service changes.
C.
Enable the Audit account management policy in the Default Domain Controller Policy.
D.
Run auditpol.exe and then enable the Audit directory service access setting in the Default
Domain policy.
Explanation:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc731607%28v=ws.10%29.aspx
AD DS Auditing Step-by-Step Guide
In Windows Server 2008 you can now set up AD DS auditing with a new audit subcategory
to log old and new values when changes are made to objects and their attributes.
..
The ability to audit changes to objects in AD DS is enabled with the new audit policy
subcategory Directory Service Changes. This guide provides instructions for implementing
this audit policy subcategory.
The types of changes that you can audit include a user (or any security principal) creating,
modifying, moving, or undeleting an object. The new audit policy subcategory adds the
following capabilities to auditing in AD DS:
When a successful modify operation is performed on an attribute, AD DS logs the previous
and current values of the attribute. If the attribute has more than one value, only the values
that change as a result of the modify operation are logged.
If a new object is created, values of the attributes that are populated at the time of creation
are logged. If the user adds attributes during the create operation, those new attribute values
are logged. In most cases, AD DS assigns default values to attributes (such as
samAccountName). The values of such system attributes are not logged.
If an object is moved, the previous and new location (distinguished name) is logged for
moves within the domain. When an object is moved to a different domain, a create event is
generated on the domain controller in the target domain.
If an object is undeleted, the location where the object is moved to is logged. In addition, if
the user adds, modifies, or deletes attributes while performing an undelete operation, the
values of those attributes are logged.
..
In Windows Server 2008, you implement the new auditing feature by using the following
controls:
Global audit policy
System access control list (SACL)
Schema
Global audit policy
Enabling the global audit policy, Audit directory service access, enables all directory service
policy subcategories. You can set this global audit policy in the Default Domain Controllers
Group Policy (under Security Settings\Local Policies\Audit Policy). In Windows Server 2008,
this global audit policy is not enabled by default. Although the subcategory Directory Service
Access is enabled for success events by default, the other subcategories are not enabled by
default.
You can use the command-line tool Auditpol.exe to view or set audit policy subcategories.
There is no
Windows interface tool available in Windows Server 2008 to view or set audit policy
subcategories.
Further information:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc731451%28v=ws.10%29.aspx
Auditpol
Displays information about and performs functions to manipulate audit policies.
http://servergeeks.wordpress.com/2012/12/31/auditing-directory-services/
AD Scenario – Auditing Directory Services
Auditing of Directory Services depends on several controls, these are:1. Global Audit Policy (at category level using gpmc.msc tool)
2. Individual Audit Policy (at subcategory level using auditpol.exe tool)
3. System ACLs – to specify which operations are to be audited for a security principal.
4. Schema (optional) – this is an additional control in the schema that you can use to create
exceptions to what is audited.
In Windows Server 2008, you can now set up AD DS (Active Directory Domain Services)
auditing with a new audit policy subcategory (Directory Service Changes) to log old and new
values when changes are made to AD DS objects and their attributes. This can be done
using auditpol.exe tool.
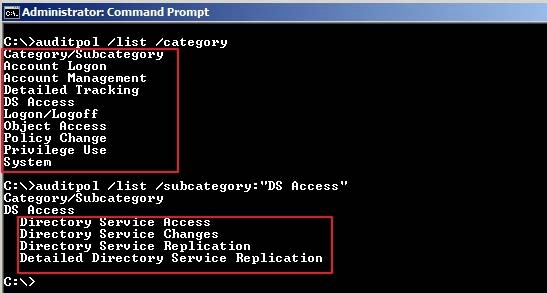
Command to check which audit policies are active on your machine: auditpol /get /category:*Command to view the audit policy categories and Subcategories:
How to enable the global audit policy using the Windows interface i.e. gpmc tool
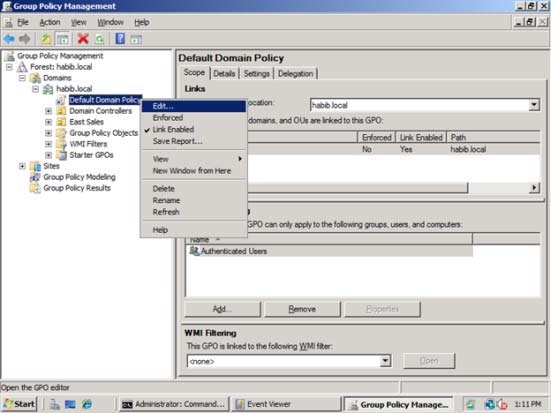
Click Start, point to Administrative Tools, and then Group Policy Management or run
gpmc.msc command.
In the console tree, double-click the name of the forest, double-click Domains, double-click
the name of your domain, double-click Domain Controllers, right-click Default Domain
Controllers Policy, and then click Edit.
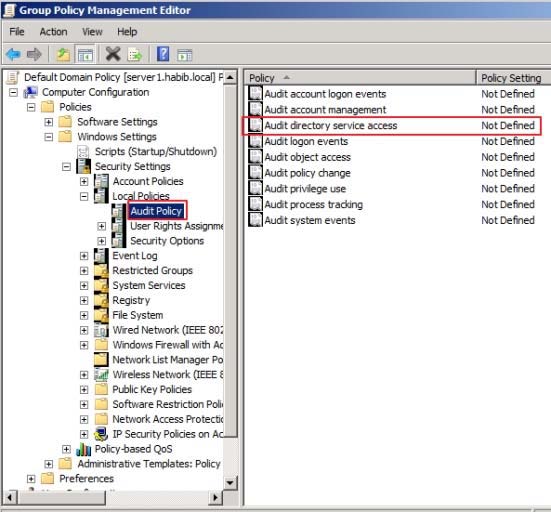
Under Computer Configuration, double-click Policies, double-click Windows Settings,
double-click Security Settings, double-click Local Policies, and then click Audit Policy.In the details pane, right-click Audit directory service access, and then click Properties.
Select the Define these policy settings check box.
Under Audit these attempts, select the Success, check box, and then click OK.How to enable the change auditing policy using a command line
Click Start, right-click Command Prompt, and then click Run as administrator.
Type the following command, and then press ENTER:
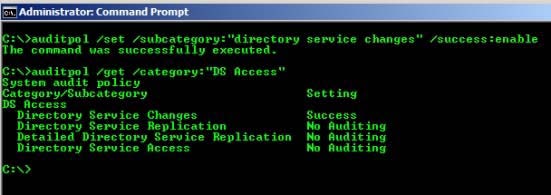
auditpol /set /subcategory:”directory service changes” /success:enable
To verify if the auditing is enabled or not for “Directory Service Changes”, you can run below
command:
auditpol /get /category:”DS Access”How to set up auditing in object SACLs
Click Start, point to Administrative Tools, and then click Active Directory Users and
Computers.
Right-click the organizational unit (OU) (or any object) for which you want to enable auditing,
and then click Properties.
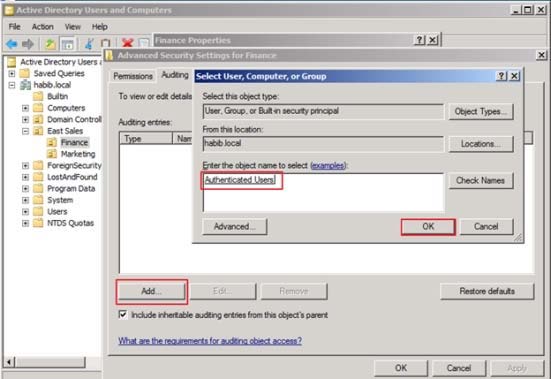
Click the Security tab, click Advanced, and then click the Auditing tab.Click Add, and under Enter the object name to select, type Authenticated Users (or any other
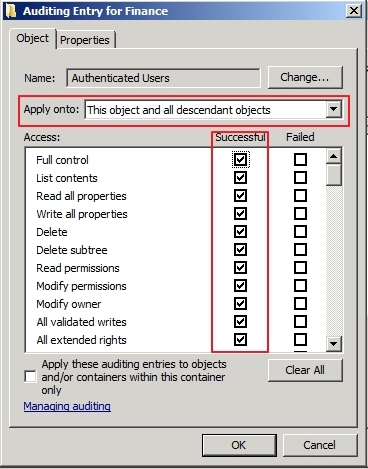
security principal) and then click OK.In Apply onto, click Descendant User objects (or any other objects).
Under Access, select the Successful check box for Write all properties.
Click OKClick OK until you exit the property sheet for the OU or other object.
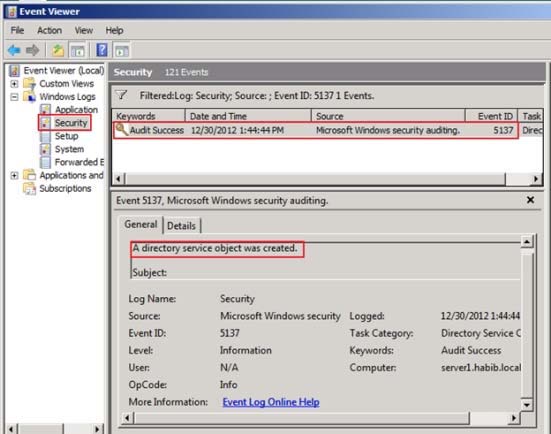
To Test whether auditing is working or not, try creating or modifying objects in Finance OU
and check the Security event logs.
I just created a new user account in Finance OU named f4.If you check the security event logs you will find eventid 5137 (Create)
Note:
Once the auditing is enabled these eventids will appear in security event logs: 5136 (Modify),
5137 (Create), 5138 (Undelete), 5139 (Move).