You are the network administrator for an organization that has two locations, New York and
London.
Each location has multiple domains but all domains fall under the same tree, Stellacon.com.
Users in the NY.us.stellacon.com domain need to access resources in the
London.uk.stellacon.comdomain.
You need to reduce the amount of time it takes for authentication when users from
NY.us.stellacon.com access resources in London.uk.stellacon.com.
What can you do?

A.
Set up a one-way shortcut trust from London.uk.stellacon.com to NY.us.stellacon.com.
B.
Set up a one-way shortcut trust from NY.us.stellacon.com to London.uk.stellacon.com.
C.
Enable Universal Group Membership Caching in NY.us.stellacon.com.
D.
Enable Universal Group Membership Caching in London.uk.stellacon.com.
Explanation:
Basically the same as B/Q7.
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc754538.aspx
Understanding When to Create a Shortcut Trust
When to create a shortcut trust
Shortcut trusts are one-way or two-way, transitive trusts that administrators can use to
optimize the authentication process.
Authentication requests must first travel a trust path between domain trees. In a complex
forest this can take time, which you can reduce with shortcut trusts. A trust path is the series
of domain trust relationships that authentication requests must traverse between any two
domains. Shortcut trusts effectively shorten the path that authentication requests travel
between domains that are located in two separate domain trees.
Shortcut trusts are necessary when many users in a domain regularly log on to other
domains in a forest.
Using the following illustration as an example, you can form a shortcut trust between domain
B and domain D, between domain A and domain 1, and so on.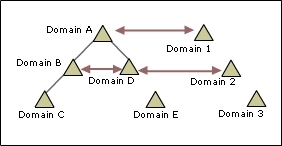
Using one-way trusts
A one-way, shortcut trust that is established between two domains in separate domain trees
can reduce the time that is necessary to fulfill authentication requests—but in only one
direction. For example, when a oneway, shortcut trust is established between domain A and
domain B, authentication requests that are made in domain A to domain B can use the new
one-way trust path. However, authentication requests that are made in domain B to domain
A must still travel the longer trust path.
Using two-way trusts
A two-way, shortcut trust that is established between two domains in separate domain trees
reduces the time that is necessary to fulfill authentication requests that originate in either
domain. For example, when a two-way trust is established between domain A and domain B,
authentication requests that are made from either domain to the other domain can use the
new, two-way trust path.


