###BeginCaseStudy###
Testlet 1
Topic 5, Proseware, Inc
Overview
General Overview
Proseware, Inc., is an international manufacturing company that has 3,000 users. Proseware has a sales
department, a marketing department, a research department, and a human resources department.
Proseware recently purchased a small competitor named Contoso, Ltd.
Physical Locations
Proseware has two offices. The offices are located in New York and London. The offices connect to each other
by using a WAN link. Each office connects directly to the Internet.
Contoso has one office in Chicago.
Existing Environment
Active Directory Environment
The network of Proseware contains an Active Directory forest named proseware.com. The forest contains a
single domain and two sites named London and New York. Each site contains two domain controllers that run
Windows Server 2008 R2. The domain controllers in the New York site are named DC1 and DC2. The domain
controllers in the London site are named DC3 and DC4.
All FSMO roles are hosted on DC3 and DC4.
The network of Contoso contains an Active Directory forest named contoso.com. The forest contains five
domain controllers and one site.
Exchange Server Organization
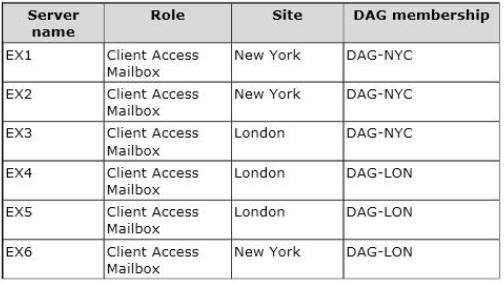
Proseware has an Exchange Server 2013 organization that contains two database availability groups (DAGs)
named DAG-NYC and DAG-LON. The DAGs are configured as shown in the following table.
The certificate used for Exchange Server 2013 has a subject name of mail.proseware.com and a Subject
Alternative Name (SAN) of autodiscover.proseware.com.
Each mailbox database has three copies. All users connect to an active copy of the database on a server in
their respective office. Native data protection is implemented.
NTLM communication is used exclusively for Outlook Anywhere both internally and externally.Problem Statements
Proseware identifies the following issues:
Users report that sometimes, they fail to access the free/busy information of the other users. You also
discover that some users fail to retrieve Autodiscover settings.
Users in the London office report that during a 24-hour WAN outage, they could see only new users in the
global address list (GAL) from Outlook Web App.
The manager of the human resources department in the New York office cannot see new London office
users in the GAL until several hours after the help desk confirms that the users were created.
A hung MSExchangeOWAAppPool in Internet Information Services (IIS) on EX1 causes all of the database
copies to fail over. Despite having the same CopyQueueLength and ReplayQueueLength as the copies on
EX2, the copies on EX3, which have a higher activation preference, are activated, forcing user connections
over the WAN.
A custom application named Appl recently malfunctioned and sent hundreds of false positive email
notifications that had a subject of System Alert: Sales Database Reaching Capacity to all of the users in the
organization. While attempting to remove the email messages, an administrator ran the Search-Mailbox –
DeleteContent command and erroneously deleted valid email messages from the mailboxes of some
executives.
Requirements
Business Goal
Proseware identifies the following business goals:
Reduce the costs associated with using bandwidth on the WAN links.
Improve social media integration by using a Microsoft Outlook app that will be deployed to all of the users in
the sales department.
Planned Changes
Proseware plans to make the following changes:
Implement a lagged copy for the mailbox database of the executives.
Implement an RBAC-linked role group for the administrators at Contoso to manage the mailboxes of the
Proseware users.
Technical Requirements
Proseware identifies the following technical requirements:
End users must be notified after one hour if the email messages that they send are not delivered.
If mailbox database storage fails, the IT department must be able to recover old email messages that were
sent up to five days earlier to the mailboxes of the executives.
All new users hired at Contoso must have a user account in contoso.com and an Exchange Server mailbox
in proseware.com. All new user accounts in contoso.com must have a user principal name (UPN) that ends
with proseware.com.
Administrators at Contoso must be able to create and manage recipient objects in the Exchange Server
organization of Proseware by using their existing contoso.com administrator account. All Contoso recipient
objects must reside in an organizational unit (OU) named proseware.com
Security Requirements
The Chief Security Officer (CSO) introduces the following security requirements:
All Outlook users who connect from the Internet must use Basic authentication only.
All Outlook users who connect from the internal network must use NTLM authentication only.
SLA Requirements
Due to productivity losses during some recent maintenance windows, the Chief Information Officer (CIO)
introduces a new service level agreement (SLA) requiring that all servers entering or exiting a maintenance
window must be taken in and out of service properly.
The SLA contains the following requirements:
All mounted databases on the server undergoing maintenance must be activated on another server.
All message queues on the server undergoing maintenance must be empty before maintenance can begin.
The server undergoing maintenance must be prevented from becoming a Primary Active Manager (PAM).Databases copies on the server undergoing maintenance must not be activated while maintenance is
occurring.
###EndCaseStudy###
HOTSPOT
You are attempting to resolve the database activation issue. You need to identify why the database copies are
activated on EX3 instead of EX2.
Which command should you use? (To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.)
Hot Area:

Explanation:
Exchange 2013 Managed Availability
http://www.msexchange.org/kbase/ExchangeServerTips/ExchangeServer2013/monitoring/exchange-2013-
managed-availability.html
This tips describes the new Managed Availability feature present in Exchange 2013.
In Exchange 2013, native, built-in monitoring and recovery actions are included in a feature called Managed
Availability. Managed Availability is the integration of built-in, active monitoring and the Exchange 2013 high
availability platform, allowing Exchange to make a determination on when to fail over a database based on
service health.
To view the health of a server, you use the cmdlets Get-ServerHealth to retrieve the raw health data and GetHealthReport that operates on the raw health data and provides a snapshot of the health.
This example returns the server health for server MBX1:
Get-ServerHealth Server01
The following examples return a report on the health of the server. The second cmdlet narrows this report to the
Store process:
Get-ServerHealth | Get-HealthReportGet-ServerHealth | Where {$_.HealthSetName -eq “Store”} GetHealthReport
Get-AvailabilityReportOutage
Use the Get-AvailabilityReportOutage cmdlet to return the daily downtime (if any) for each service entity and its
overridden value (if set) to the overall reported availability for the day.EXAMPLE 1
This example returns all outages that occurred the previous day. This cmdlet always returns outages for one
day.
Get-AvailabilityReportOutage
EXAMPLE 2
This example returns all outages reported for Microsoft Outlook services at all sites on the selected day.
Get-AvailabilityReportOutage -ReportDate:”2011-12-05″ -Identity:”Outlook*”
Get-HealthReport
Use the Get-HealthReport cmdlet to return health information related to the server you specify. You can use the
health values to determine the state of the server.The cmdlet also returns an alert value that provides the
specific state of your server.
This example retrieves health information about a server running Microsoft Exchange Server 2013.
Get-HealthReport -RollupGroup
The following list contains the health values that are returned:
Online
Partially Online
Offline
Sidelined
Functional
Unavailable
Get-ServerHealth
Use the Get-ServerHealth cmdlet to return health information related to the server you specify.
This example returns the server health for server Server01.
Get-ServerHealth -Identity Server01
The cmdlet also returns an alert value that provides the specific state of your server. The following values may
be returned:
Degraded
Unhealthy
Repairing
Disabled
Unavailable
UnInitialized
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/jj218703(v=exchg.150).aspx