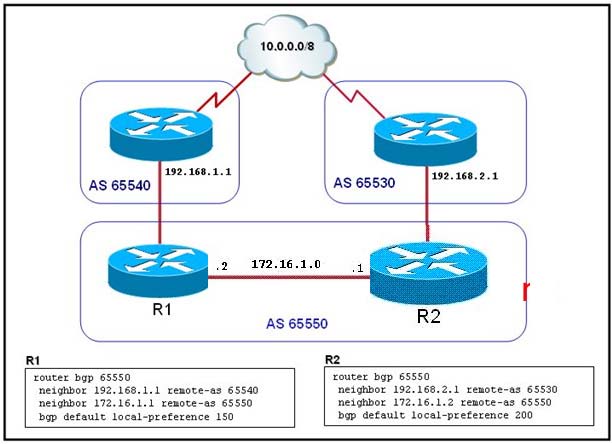
Refer to the exhibit. Network 10.0.0.0/8 is being advertised to autonomous system 65550 via
both external links. Which statement about the preferred path to the 10.0.0.0/8 network is
true?

A.
Router R2 will be preferred because it has the higher neighbor IP address.
B.
Router R2 will be preferred because its neighbor has a lower autonomous system
number.
C.
Router R1 will be preferred because it has a lower local preference.
D.
Router R2 will be preferred because it has a higher local preference.
E.
Router R1 will be preferred because its neighbor has the higher autonomous system
number.
F.
Router R1 will be preferred because it has the lower neighbor IP address.
Explanation:
The preferred path to 10.0.0.0/8 network is R2 because it has a higher local preference.
The following process summarizes how BGP chooses the best route on a Cisco router.
• Prefer the route with the highest weight. (The weight attribute is proprietary to Cisco
and is local to the router only.)
• If multiple routes have the same weight, prefer the route with the highest local
preference value. (The local preference is used within an autonomous system.)
• If multiple routes have the same local preference, prefer the route that the local
router originated. A locally originated route has a next hop of 0.0.0.0 in the BGP table.
• If none of the routes were locally originated, prefer the route with the shortest
autonomous system path.
• If the autonomous system path length is the same, prefer the lowest origin code (IGP
< EGP < incomplete).
• If all origin codes are the same, prefer the path with the lowest MED. (The MED is
exchanged between autonomous systems.) The MED comparison is made only if the
neighboring autonomous system is the same for all routes considered, unless the bgp
always-compare-med command is enabled
• If the routes have the same MED, prefer external paths to internal paths.
• If synchronization is disabled and only internal paths remain, prefer the path through
the closest IGP neighbor, which means that the router prefers the shortest internal path
within the autonomous system to reach the destination (the shortest path to the BGP next
hop).
• For EBGP paths, select the oldest route to minimize the effect of routes going up and
down (flapping).
• Prefer the route with the lowest neighbor BGP router ID value.
• If the BGP router IDs are the same, prefer the router with the lowest neighbor IP
address.
In this example, since the weights remained the same (default) value the next thing that is
looked at is the highest local preference.