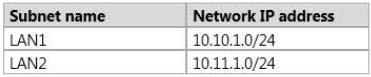
Your network contains two subnets. The subnets are configured as shown in the following table.
You have a server named Server1 that runs Windows Server 2012 R2. Server1 is connected to LAN1.
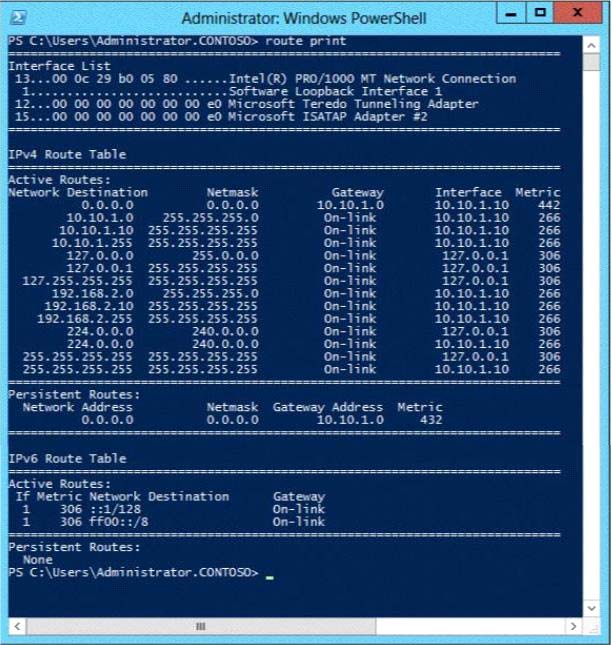
You run the route print command as shown in the exhibit. (Click the Exhibit button.)
You need to ensure that Server1 can communicate with the client computers on LAN2.
What should you do?

A.
Change the default gateway address.
B.
Set the state of the Microsoft ISATAP Adapter #2 interface to disable.
C.
Change the metric of the 10.10.1.0 route.
D.
Set the state of the Teredo interface to disable.
Explanation:
The exhibit shows the default gateway address to be that of LAN1. This should be changed to the
LAN2 gateway address to allow client computers access on LAN2.
In general, the first and last addresses in a subnet are used as the network identifier and broadcast
address, respectively. All other addresses in the subnet can be assigned to hosts on that subnet. For
example, IP addresses of networks with subnet masks of at least 24 bits ending in .0 or .255 can
never be assigned to hosts. Such “last” addresses of a subnet are considered “broadcast” addresses
and all hosts on the corresponding subnet will respond to it. Theoretically, there could be situations
where you can assign an address ending in .0: for example, if you have a subnet like
192.168.0.0/255.255.0.0, you are allowed to assign a host the address 192.168.1.0. It could create
confusion though, so it’s not a very common practice.
Example10.6.43.0 with subnet 255.255.252.0 (22 bit subnet mask) means subnet ID 10.6.40.0, a host
address range from 10.6.40.1 to 10.6.43.254 and a broadcast address10.6.43.255. So in theory, your
example 10.6.43.0 would be allowed as a valid host address. The default gateway address should not
end in .0 with the /24 address.
References:
Training Guide: Installing and Configuring Windows Server 2012 R2, Chapter 4: Deploying domain
controllers, Lesson 4: Configuring IPv6/IPv4 Interoperability, p. 254-256