ISO 9126 is a standard to assist in evaluating the quality of a product. Which of the following is defined as a set of attributes that bear on the existence of a set of functions and their specified properties?
A. Reliability
B. Usability
C. Functionality
D. Maintainability
Functionality – A set of attributes that bear on the existence of a set of functions and their specified properties.
The functions are those that satisfy stated or implied needs.
Suitability
Accuracy
Interoperability
Security
Functionality Compliance
For CISA Exam you should know below information about ISO 9126 model:
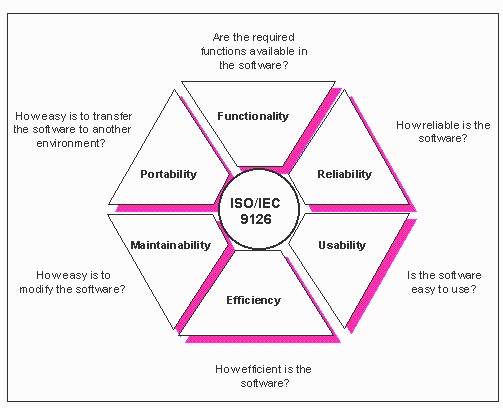
ISO/IEC 9126 Software engineering -” Product quality was an international standard for the evaluation of software quality. It has been replaced by ISO/IEC 25010:2011.[1] The fundamental objective of the ISO/IEC 9126 standard is to address some of the well-known human biases that can adversely affect the delivery and perception of a software development project. These biases include changing priorities after the start of a project or not having any clear definitions of -success.- By clarifying, then agreeing on the project priorities and subsequently converting abstract priorities (compliance) to measurable values (output data can be validated against schema X with zero intervention), ISO/IEC 9126 tries to develop a common understanding of the projects objectives and goals.
ISO 9126
Image above from: http://www.cse.dcu.ie/essiscope/sm2/9126ref1.gif
The standard is divided into four parts:
Quality model
External metrics
Internal metrics
Quality in use metrics.
Quality Model
The quality model presented in the first part of the standard, ISO/IEC 9126-1,[2] classifies software quality in a structured set of characteristics and sub-characteristics as follows:
Functionality – A set of attributes that bear on the existence of a set of functions and their specified properties. The functions are those that satisfy stated or implied needs.
Suitability
Accuracy
Interoperability
Security
Functionality Compliance
Reliability – A set of attributes that bear on the capability of software to maintain its level of performance under stated conditions for a stated period of time.
Maturity
Fault Tolerance
Recoverability
Reliability Compliance
Usability – A set of attributes that bear on the effort needed for use, and on the individual assessment of such use, by a stated or implied set of users.
Understandability
Learn ability
Operability
Attractiveness
Usability Compliance
Efficiency – A set of attributes that bear on the relationship between the level of performance of the software and the amount of resources used, under stated conditions.
Time Behavior
Resource Utilization
Efficiency Compliance
Maintainability – A set of attributes that bear on the effort needed to make specified modifications.
Analyzability
Changeability
Stability
Testability
Maintainability Compliance
Portability – A set of attributes that bear on the ability of software to be transferred from one environment to another.
Adaptability
Install ability
Co-Existence
Replace ability
Portability Compliance
Each quality sub-characteristic (e.g. adaptability) is further divided into attributes. An attribute is an entity which can be verified or measured in the software product. Attributes are not defined in the standard, as they vary between different software products.
Software product is defined in a broad sense: it encompasses executables, source code, architecture descriptions, and so on. As a result, the notion of user extends to operators as well as to programmers, which are users of components such as software libraries.
The standard provides a framework for organizations to define a quality model for a software product. On doing so, however, it leaves up to each organization the task of specifying precisely its own model. This may be done, for example, by specifying target values for quality metrics which evaluates the degree of presence of quality attributes.
Internal Metrics
Internal metrics are those which do not rely on software execution (static measure)
External Metrics
External metrics are applicable to running software.
Quality in Use Metrics
Quality in use metrics are only available when the final product is used in real conditions.
Ideally, the internal quality determines the external quality and external quality determines quality in use.
This standard stems from the GE model for describing software quality, presented in 1977 by McCall et al., which is organized around three types of Quality Characteristics:
Factors (To specify): They describe the external view of the software, as viewed by the users.
Criteria (To build): They describe the internal view of the software, as seen by the developer.
Metrics (To control): They are defined and used to provide a scale and method for measurement.
ISO/IEC 9126 distinguishes between a defect and a nonconformity, a defect being The nonfulfillment of intended usage requirements, whereas a nonconformity is The nonfulfillment of specified requirements. A similar distinction is made between validation and verification, known as V&V in the testing trade.
The following were incorrect answers:
Reliability – A set of attributes that bear on the capability of software to maintain its level of performance under stated conditions for a stated period of time.
Usability – A set of attributes that bear on the effort needed for use, and on the individual assessment of such use, by a stated or implied set of users.
Maintainability – A set of attributes that bear on the effort needed to make specified modifications.
The following reference(s) were/was used to create this question:
CISA review manual 2014 Page number 188