Your network contains an Active Directory domain named contoso.com. The network contains 500 client
computers that run Windows 8. All of the client computers connect to the Internet by using a web proxy.
You deploy a server named Server1 that runs Windows Server 2012 R2. Server1 has the DNS Server server
role installed.
You configure all of the client computers to use Server1 as their primary DNS server. You need to preventServer1 from attempting to resolve Internet host names for the client computers.
What should you do on Server1?

A.
Create a primary zone named “.”.
B.
Configure the Security settings of the contoso.com zone.
C.
Create a zone delegation for GlobalNames.contoso.com.
D.
Create a stub zone named “root”.
Explanation:
When you install DNS on a Windows server that does not have a connection to the Internet, the zone for the
domain is created and a root zone, also known as a dot zone, is also created. This root zone may prevent
access to the Internet for DNS and for clients of the DNS. If there is a root zone, there are no other zones other
than those that are listed with DNS, and you cannot configure forwarders or root hint servers.
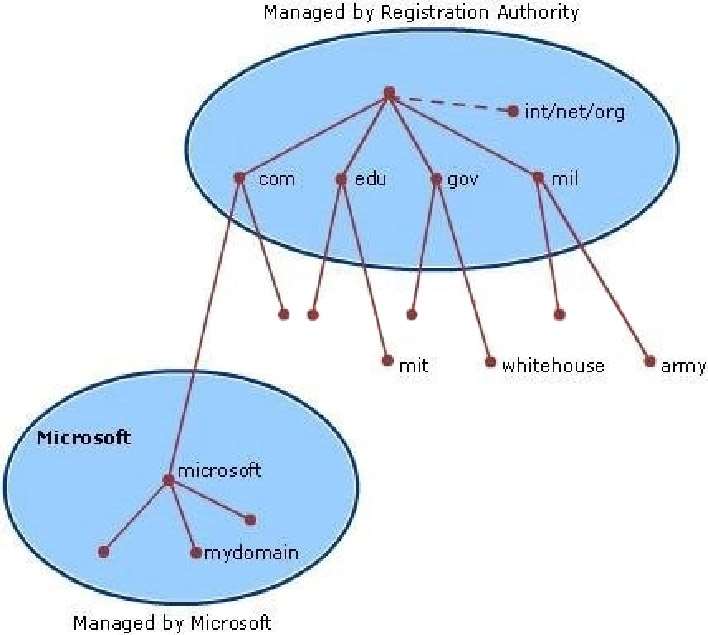
Root domain
This is the top of the tree, representing an unnamed level; it is sometimes shown as two empty quotation marks
(“”), indicating a null value. When used in a DNS domain name, it is stated by a trailing period (.) to designate
that the name is located at the root or highest level of the domain hierarchy. In this instance, the DNS domain
name is considered to be complete and points to an exact location in the tree of names. Names stated this way
are called fully qualified domain names (FQDNs).
DNS Domain Name Hierarchy: