What is the term for a logical SAN which provides isolation among devices physically connected to the same fabric?

A.
ISL
B.
IVR
C.
VoQ
D.
VSAN
E.
Enhanced ISL
Explanation:
A VSAN is a virtual storage area network (SAN). A SAN is a dedicated network that interconnects hosts and storage devices primarily to exchange SCSI traffic. In
SANs you use the physical links to make these interconnections. A set of protocols run over the SAN to handle routing, naming, and zoning. You can design multiple
SANs with different topologies.
With the introduction of VSANs, the network administrator can build a single topology containing switches, links, and one or more VSANs. Each VSAN in this
topology has the same behavior and property of a SAN. A VSAN has the following additional features:
•Multiple VSANs can share the same physical topology.
•The same Fibre Channel IDs (FC IDs) can be assigned to a host in another VSAN, thus increasing VSAN scalability.
•Every instance of a VSAN runs all required protocols such as FSPF, domain manager, and zoning.
•Fabric-related configurations in one VSAN do not affect the associated traffic in another VSAN.•Events causing traffic disruptions in one VSAN are contained within that VSAN and are not propagated to other VSANs.
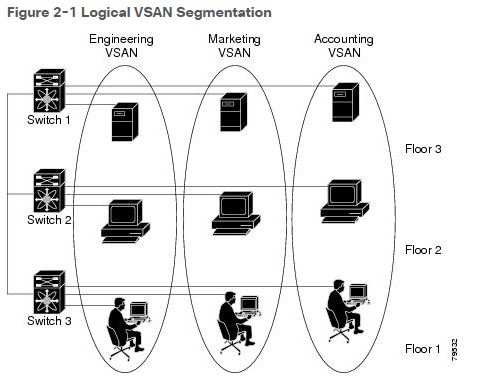
Figure 2-1 shows a fabric with three switches, one on each floor. The geographic location of the switches and the attached devices is independent of their
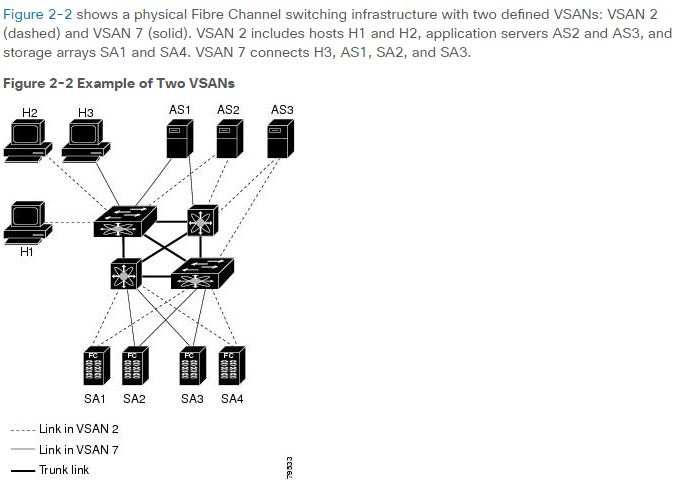
segmentation into logical VSANs. No communication between VSANs is possible. Within each VSAN, all members can talk to one another.Figure 2-2 shows a physical Fibre Channel switching infrastructure with two defined VSANs: VSAN 2 (dashed) and VSAN 7 (solid). VSAN 2 includes hosts H1 and
H2, application servers AS2 and AS3, and storage arrays SA1 and SA4. VSAN 7 connects H3, AS1, SA2, and SA3.Without VSANs, a network administrator would need separate switches and links for separate SANs. By enabling VSANs, the same switches and links may be
shared by multiple VSANs. VSANs allow SANs to be built on port granularity instead of switch granularity.
VSAN Advantages
•Traffic isolation—Traffic is contained within VSAN boundaries and devices reside only in one VSAN ensuring absolute separation between user groups, if desired.
•Scalability—VSANs are overlaid on top of a single physical fabric. The ability to create several logical VSAN layers increases the scalability of the SAN.
•Per VSAN fabric services—Replication of fabric services on a per VSAN basis provides increased scalability and availability.
•Redundancy—Several VSANs created on the same physical SAN ensure redundancy. If one VSAN fails, redundant protection (to another VSAN in the same
physical SAN) is configured using a backup path between the host and the device.•Ease of configuration—Users can be added, moved, or changed between VSANs without changing the physical structure of a SAN. Moving a device from one
VSAN to another only requires configuration at the port level, not at a physical level.
Up to 256 VSANs can be configured in a switch. Of these, one is a default VSAN (VSAN 1), and another is an isolated VSAN (VSAN 4094). User-specified VSAN
IDs range from 2 to 4093.