Which of the following BEST describes a block cipher?

A.
An asymmetric key algorithm that operates on a variable-length
block of plaintext and transforms it into a fixed-length block of
ciphertext
B.
A symmetric key algorithm that operates on a fixed-length block of
plaintext and transforms it into a fixed-length block of ciphertext
C.
An asymmetric key algorithm that operates on a fixed-length block
of plaintext and transforms it into a fixed-length block of ciphertext
D.
A symmetric key algorithm that operates on a variable-length block
of plaintext and transforms it into a fixed-length block of ciphertext
Explanation:
A block cipher breaks the plaintext into fixed-length blocks, commonly
64-bits, and encrypts the blocks into fixed-length blocks of
ciphertext. Another characteristic of the block cipher is that, if the
same key is used, a particular plaintext block will be transformed
into the same ciphertext block. Examples of block ciphers are DES,
Skipjack, IDEA, RC5 and AES. An example of a block cipher in a symmetric
key cryptosystem is the Electronic Code Book (ECB) mode of
operation. In the ECB mode, a plaintext block is transformed into a
ciphertext block as shown in Figure. If the same key is used for
each transformation, then a Code Book can be compiled for each
plaintext block and corresponding ciphertext block.
Answer a is incorrect since it refers to a variable-length block of
plaintext being transformed into a fixed-length block of ciphertext.
Recall that this operation has some similarity to a hash function,
which takes a message of arbitrary length and converts it into a fixedlength
message digest.
* Answers “An asymmetric key algorithm that operates on a variable-lengthblock of plaintext and transforms it into a fixed-length block of
ciphertext” and “An asymmetric key algorithm that operates on a fixed-length block
of plaintext and transforms it into a fixed-length block of ciphertext”are incorrect because they
involve asymmetric key algorithms, and the block cipher is used with
symmetric key algorithms.
Exhibit: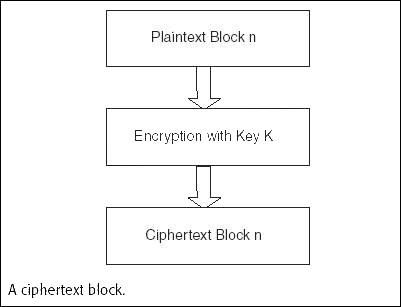
In other cryptographic modes of operation, such as Cipher Block
Chaining (CBC), the result of the encryption of the plaintext block, Pn,
is fed into the encryption process of plaintext block Pn+1. Thus, the
result of the encryption of one block affects the result of the encryption
of the next block in the sequence.


