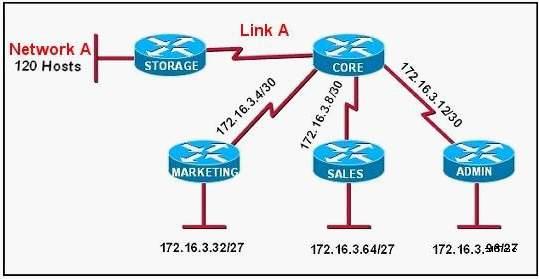
Refer to the exhibit. All of the routers in the network are configured with the ip subnet-zero
command. Which network addresses should be used for Link A and Network A? (Choose two.)

A.
Link A – 172.16.3.40/30
B.
Link A – 172.16.3.0/30
C.
Network A – 172.16.3.192/26
D.
Network A – 172.16.3.48/26
E.
Network A – 172.16.3.128/25
F.
Link A – 172.16.3.112/30
Explanation:
If a network address is subnetted, the first subnet obtained after subnetting the network address is
called subnet zero.
Consider a Class B address, 172.16.0.0. By default the Class B address 172.16.0.0 has 16 bits
reserved for representing the host portion, thus allowing 65534 (2 16 -2) valid host addresses. If
network 172.16.0.0/16 is subnetted by borrowing three bits from the host portion, eight (2 3 )
subnets are obtained. The table below is an example showing the subnets obtained by subnetting
the address 172.16.0.0, the resulting subnet mask, the corresponding broadcast addresses, and
the range of valid host addresses.
In the example above, the first subnet (subnet 172.16.0.0/19) is called subnet zero.
The class of the network subnetted and the number of subnets obtained after subnetting have no
role in determining subnet zero. It is the first subnet obtained when subnetting the network
address. Also, when you write the binary equivalent of the subnet zero address, all the subnet bits
(bits 17, 18, and 19 in this case) are zeros. Subnet zero is also known as the all-zeros subnet.
In this example, link A will use the zero subnet of 172.16.30./30, while network A will need a /25 to
support the 120 hosts. Answer C will support up to 128 (126 usable) hosts while options E and F
will only support 62 usable IP addresses.