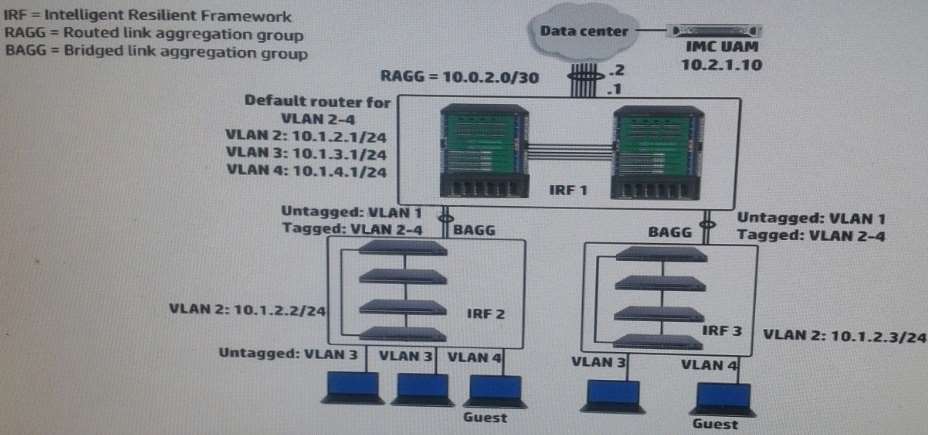
Refer to the exhibit.
A company has a functional multicast routing solution, which routes multicasts from the data center users in
VLAN3 and VLAN4. Users in VLAN 3 and VLAN 4 sometimes register for some of the same multicast. The
network administrator wants to prevent duplicate multicasts on the link between the core IRF virtual switch and
the access layer IRF virtual switches.
What should the administrator do to accomplish this goal?

A.
Enable IGMP snooping on VLAN 3 and VLAN4 (Layer 2) on the core switch and on the access layer
switches.
B.
Create Layer 3 interfaces for VLAN 3 and VLAN 4 on the access layer switches, and enable IGMP on the
interfaces.
C.
Enable Multicast VLAN and IGMP snooping on VLAN 3 on the access layer switches, and associate VLAN
4 as a sub-VLAN.
D.
Create Layer 3 interfaces for VLAN 3 and VLAN 4 on the access layer switches, and enable PIM on the
interfaces.
Explanation:
IGMP snooping is designed to prevent hosts on a local network from receiving traffic for a multicast group they
have not explicitly joined. It provides switches with a mechanism to prune multicast traffic from links that do not
contain a multicast listener (an IGMP client).
IGMP snooping is the process of listening to Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) network traffic. The
feature allows a network switch to listen in on the IGMP conversation between hosts and routers. By listening to
these conversations the switch maintains a map of which links need which IP multicast streams. Multicasts may
be filtered from the links which do not need them and thus controls which ports receive specific multicast traffic.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/IGMP_snooping