You need to determine the correct wireless LAN topology for use in the Company network.
Which three statements are true about the various WLAN topologies? (Select three)

A.
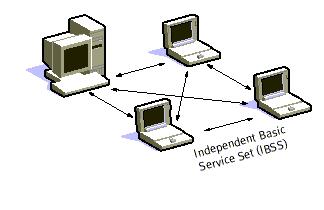
In ad hoc mode, the Independent Basic Service Set (IBSS) is a framework in which
mobile clients connect directly without an intermediate access point.
B.
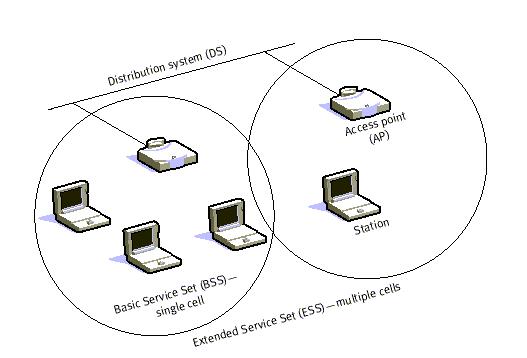
In Infrastructure mode, the Basic Service Set (BSS) is a framework in which mobile
clients use a single access point for connecting to each other or to wired network resources.
C.
In Infrastructure mode, the Extended Services Set (ESS) is a framework in which two
or more Basic Service Sets are connected by a common distribution system (DS).
D.
In Infrastructure mode, the Independent Basic Service Setet (IBSS) is a framework in
which mobile clients connect directly without an intermediate access point.
E.
In ad hoc mode, the Basic Service Set (BSS) is a framework in which mobile clients
use a single AP for connecting to each other or to wired network resources.
F.
In ad hoc mode, the Extended Services Set (ESS) is a framework in which two or
more Basic Service Sets are connected by a common distribution system (DS)
Explanation:
A BSS that stands alone and is not connected to a base is called an Independent Basic
Service Set (IBSS) or is referred to as an Ad-Hoc Network. An ad-hoc network is a network
where stations communicate only peer to peer. There is no base and no one gives
permission to talk. Mostly these networks are spontaneous and can be set up rapidly. AdHoc or IBSS networks are characteristically limited both temporally and spatially.Fig 1: “Adhoc Mode”
When BSS’s are interconnected the network becomes one with infrastructure. 802.11
infrastructure has several elements. Two or more BSS’s are interconnected using a
Distribution System or DS. This concept of DS increases network coverage. Each BSS
becomes a component of an extended, larger network. Entry to the DS is accomplished with
the use of Access Points (AP). An access point is a station, thus addressable. So, data
moves between the BSS and the DS with the help of these access points.
Creating large and complex networks using BSS’s and DS’s leads us to the next level of
hierarchy, the Extended Service Set or ESS. The beauty of the ESS is the entire network
looks like an independent basic service set to the Logical Link Control layer (LLC). This
means that stations within the ESS can communicate or even move between BSS ′s
transparently to the LLC.Fig 2: Infrastructure Mode
http://www.tutorial-reports.com/wireless/wlanwifi/wifi_architecture.php