Which OSPF LSA type does an ASBR use to originate a default route into an area? (Exhibit)

A.
LSA 1
B.
LSA 3
C.
LSA 4
D.
LSA 5
E.
LSA 7
Explanation:
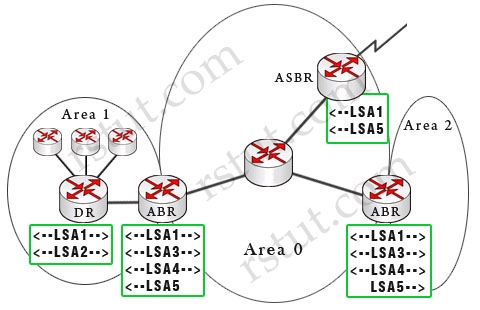
Type 5 external link LSAs are used to advertise external routes originated from an ASBR. They are flooded through the whole OSPF domain.(Note: The dashed arrows show the directions of LSAs in this example)
Below is a summary of OSPF Link-state advertisements (LSAs)
Router link LSA (Type 1) Each router generates a Type 1 LSA that lists its neighbors and the cost to each. LSA Type 1 is only flooded inside the routers area, does not cross ABR.
Network link LSA (Type 2) is sent out by the designated router (DR) and lists all the routers on the segment it is adjacent to. Types 2 are ?ooded within its area only; does not cross ABR.
Type 1 & type 2 are the basis of SPF path selection.Summary link LSA (Type 3) ABRs generate this LSA to send between areas (so type 3 is called inter-area link). It lists the networks inside other areas but still belonging to the autonomous system and aggregates routes.
Summary links are injected by the ABR from the backbone into other areas and from other areas into the backbone.Summary LSA (Type 4) Generated by the ABR to describe routes to ASBRs. In the above example, the only ASBR belongs to area 0 so the two ABRs send LSA Type 4 to area 1 & area 2 (not vice versa).
This is an indication of the existence of the ASBR in area 0. Note: Type 4 LSAs contain the router ID of the ASBR.External Link LSA (LSA 5) Generated by ASBR to describe routes redistributed into the area (which means networks from other autonomous systems). These routes appear as E1 or E2 in the routing table.
E2 (default) uses a static cost throughout the OSPF domain as it only takes the cost into account that is reported at redistribution. E1 uses a cumulative cost of the cost reported into the
OSPF domain at redistribution plus the local cost to the ASBR. Type 5 LSAs flood throughout the entire autonomous system but notice that Stubby Area and Totally Stubby Area do not accept Type 5.Multicast LSA (Type 6) are specialized LSAs that are used in multicast OSPF applications.
NSSA External LSA (Type 7) Generated by an ASBR inside a NSSA to describe routes redistributed into the NSSA. LSA 7 is translated into LSA 5 as it leaves the NSSA.
These routes appear as N1 or N2 in the ip routing table inside the NSSA. Much like LSA 5, N2 is a static cost while N1 is a cumulative cost that includes the cost upto the ASBRReference: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk365/technologies_white_paper09186a0080094e9e.shtml#appa1

