What is the solution to the fault condition?
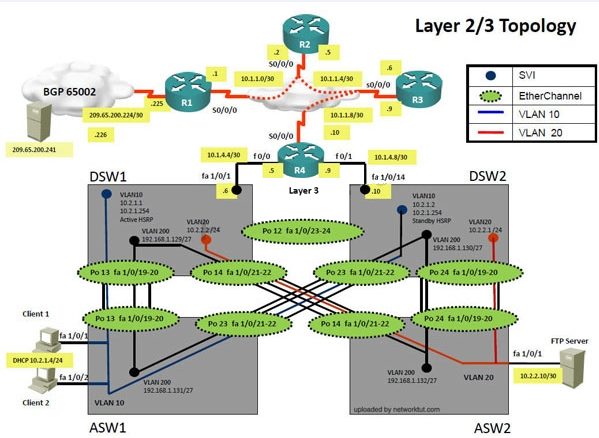
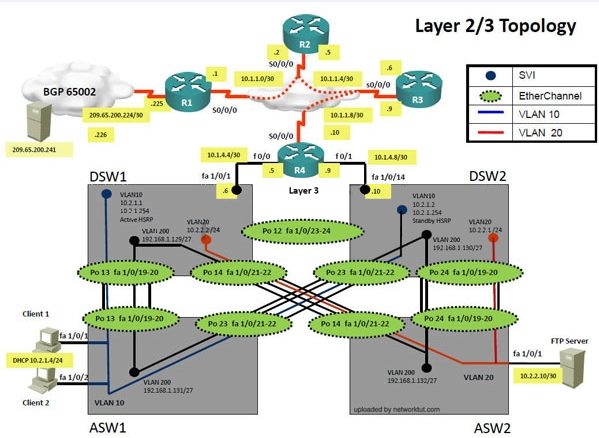
Topology Overview (Actual Troubleshooting lab design is for below network design)
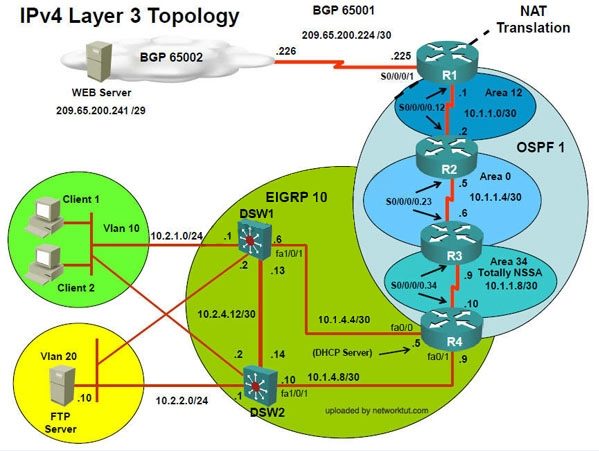
Client Should have IP 10.2.1.3
EIGRP 100 is running between switch DSW1 & DSW2
OSPF (Process ID 1) is running between R1, R2, R3, R4
Network of OSPF is redistributed in EIGRP
BGP 65001 is configured on R1 with Webserver cloud AS 65002
HSRP is running between DSW1 & DSW2 Switches
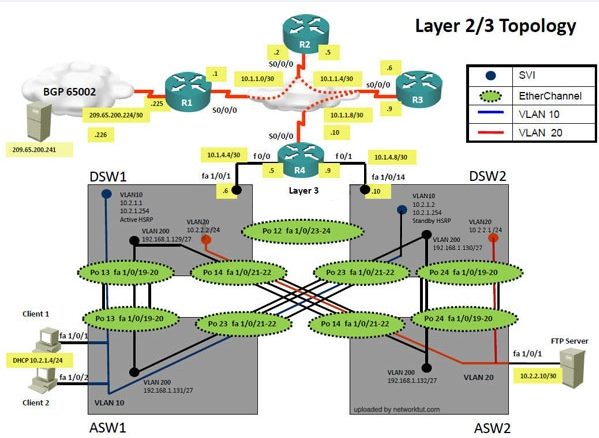
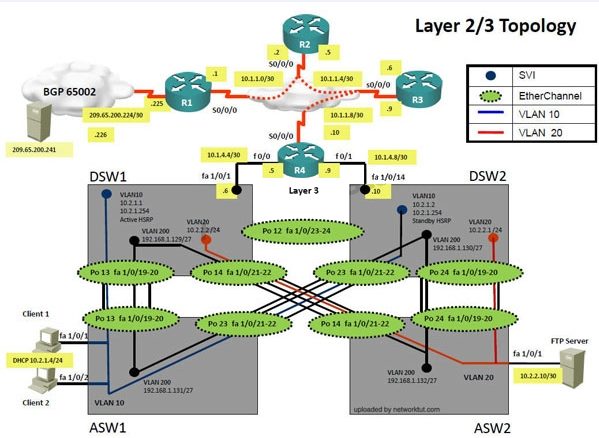
The company has created the test bed shown in the layer 2 and layer 3 topology exhibits.
This network consists of four routers, two layer 3 switches and two layer 2 switches.
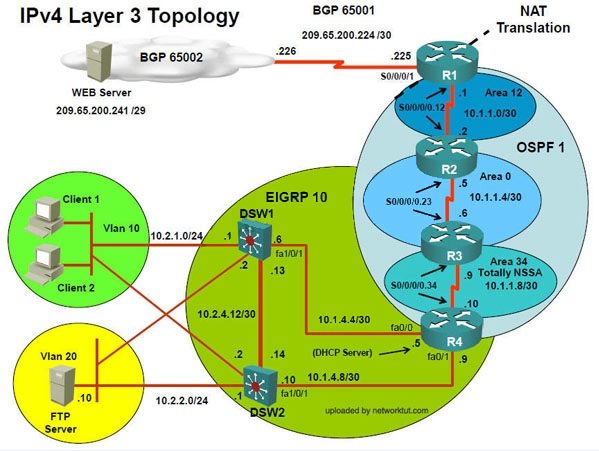
In the IPv4 layer 3 topology, R1, R2, R3, and R4 are running OSPF with an OSPF process
number 1.
DSW1, DSW2 and R4 are running EIGRP with an AS of 10. Redistribution is enabled where
necessary.
R1 is running a BGP AS with a number of 65001. This AS has an eBGP connection to AS 65002
in the ISP’s network. Because the company’s address space is in the private range.
R1 is also providing NAT translations between the inside (10.1.0.0/16 & 10.2.0.0/16) networks and
outside (209.65.0.0/24) network.
ASW1 and ASW2 are layer 2 switches.
NTP is enabled on all devices with 209.65.200.226 serving as the master clock source.
The client workstations receive their IP address and default gateway via R4’s DHCP server.
The default gateway address of 10.2.1.254 is the IP address of HSRP group 10 which is running
on DSW1 and DSW2.
In the IPv6 layer 3 topology R1, R2, and R3 are running OSPFv3 with an OSPF process number
6.
DSW1, DSW2 and R4 are running RIPng process name RIP_ZONE.
The two IPv6 routing domains, OSPF 6 and RIPng are connected via GRE tunnel running over the
underlying IPv4 OSPF domain. Redistrution is enabled where necessary.
Recently the implementation group has been using the test bed to do a ‘proof-of-concept’ on
several implementations. This involved changing the configuration on one or more of the devices.
You will be presented with a series of trouble tickets related to issues introduced during these
configurations.
Note: Although trouble tickets have many similar fault indications, each ticket has its own issue
and solution.
Each ticket has 3 sub questions that need to be answered & topology remains same.
Question-1Fault is found on which device,
Question-2Fault condition is related to,
Question-3What exact problem is seen & what needs to be done for solution
=============================================
–Client is unable to ping IP 209.65.200.241
Solution
Steps need to follow as below:-When we check on client 1 & Client 2 desktop we are not receiving DHCP address from R4
Ipconfig —– Client will be getting 169.X.X.X
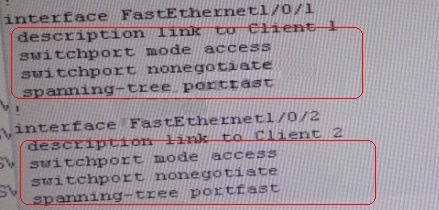
On ASW1 port Fa1/0/ 1 & Fa1/0/2 access port VLAN 10 was assigned which is using IP address
10.2.1.0/24
Sh run ——- & check for running config of int fa1/0/1 & fa1/0/2
====================================================
–====================================================
Here we are not able to see access Vlan10 configured for Port Fa1/0/1 & Fa1/0/2
Change required:On ASW1, for configuring Access Vlan under interface fa1/0/1 & 1/0/2 we
have to enable command switchport access vlan 10
————————————————
So in ticket Answer to the fault condition will be as:
The implementations group has been using the test bed to do a ‘proof-of-concept’ that
requires both Client 1 and Client 2 to access the WEB Server at 209.65.200.241. After
several changes to the network addressing, routing scheme, DHCP services, NTP services,
layer 2 connectivity, FHRP services, and device security, a trouble ticket has been opened
indicating that Client 1 cannot ping the 209.65.200.241 address.
Use the supported commands to isolated the cause of this fault and answer the following
questions.
What is the solution to the fault condition?
The fault condition is related to switch technology?
Topology Overview (Actual Troubleshooting lab design is for below network design)
Client Should have IP 10.2.1.3
EIGRP 100 is running between switch DSW1 & DSW2
OSPF (Process ID 1) is running between R1, R2, R3, R4
Network of OSPF is redistributed in EIGRP
BGP 65001 is configured on R1 with Webserver cloud AS 65002
HSRP is running between DSW1 & DSW2 Switches
The company has created the test bed shown in the layer 2 and layer 3 topology exhibits.
This network consists of four routers, two layer 3 switches and two layer 2 switches.
In the IPv4 layer 3 topology, R1, R2, R3, and R4 are running OSPF with an OSPF process
number 1.
DSW1, DSW2 and R4 are running EIGRP with an AS of 10. Redistribution is enabled where
necessary.
R1 is running a BGP AS with a number of 65001. This AS has an eBGP connection to AS 65002
in the ISP’s network. Because the company’s address space is in the private range.
R1 is also providing NAT translations between the inside (10.1.0.0/16 & 10.2.0.0/16) networks and
outside (209.65.0.0/24) network.
ASW1 and ASW2 are layer 2 switches.
NTP is enabled on all devices with 209.65.200.226 serving as the master clock source.
The client workstations receive their IP address and default gateway via R4’s DHCP server.
The default gateway address of 10.2.1.254 is the IP address of HSRP group 10 which is running
on DSW1 and DSW2.
In the IPv6 layer 3 topology R1, R2, and R3 are running OSPFv3 with an OSPF process number
6.
DSW1, DSW2 and R4 are running RIPng process name RIP_ZONE.
The two IPv6 routing domains, OSPF 6 and RIPng are connected via GRE tunnel running over the
underlying IPv4 OSPF domain. Redistrution is enabled where necessary.
Recently the implementation group has been using the test bed to do a ‘proof-of-concept’ on
several implementations. This involved changing the configuration on one or more of the devices.
You will be presented with a series of trouble tickets related to issues introduced during these
configurations.
Note: Although trouble tickets have many similar fault indications, each ticket has its own issue
and solution.
Each ticket has 3 sub questions that need to be answered & topology remains same.
Question-1Fault is found on which device,
Question-2Fault condition is related to,
Question-3What exact problem is seen & what needs to be done for solution
=============================================

–Client is unable to ping IP 209.65.200.241
Solution
Steps need to follow as below:-When we check on client 1 & Client 2 desktop we are not receiving DHCP address from R4
Ipconfig —– Client will be getting 169.X.X.X
On ASW1 port Fa1/0/ 1 & Fa1/0/2 access port VLAN 10 was assigned which is using IP address
10.2.1.0/24
Sh run ——- & check for running config of int fa1/0/1 & fa1/0/2
====================================================
–====================================================
Here we are not able to see access Vlan10 configured for Port Fa1/0/1 & Fa1/0/2
Change required:On ASW1, for configuring Access Vlan under interface fa1/0/1 & 1/0/2 we
have to enable command switchport access vlan 10
————————————————
So in ticket Answer to the fault condition will be as:
The implementations group has been using the test bed to do a ‘proof-of-concept’ that requires
both Client 1 and Client 2 to access the WEB Server at 209.65.200.241. After several changes to
the network addressing, routing scheme, DHCP services, NTP services, layer 2 connectivity,
FHRP services, and device security, a trouble ticket has been opened indicating that Client 1
cannot ping the 209.65.200.241 address.
Use the supported commands to isolated the cause of this fault and answer the following
questions.
The fault condition is related to switch technology?
which device is the fault condition located?
Topology Overview (Actual Troubleshooting lab design is for below network design)
Client Should have IP 10.2.1.3
EIGRP 100 is running between switch DSW1 & DSW2
OSPF (Process ID 1) is running between R1, R2, R3, R4
Network of OSPF is redistributed in EIGRP
BGP 65001 is configured on R1 with Webserver cloud AS 65002
HSRP is running between DSW1 & DSW2 Switches
The company has created the test bed shown in the layer 2 and layer 3 topology exhibits.
This network consists of four routers, two layer 3 switches and two layer 2 switches.
In the IPv4 layer 3 topology, R1, R2, R3, and R4 are running OSPF with an OSPF process
number 1.
DSW1, DSW2 and R4 are running EIGRP with an AS of 10. Redistribution is enabled where
necessary.
R1 is running a BGP AS with a number of 65001. This AS has an eBGP connection to AS 65002
in the ISP’s network. Because the company’s address space is in the private range.
R1 is also providing NAT translations between the inside (10.1.0.0/16 & 10.2.0.0/16) networks and
outside (209.65.0.0/24) network.
ASW1 and ASW2 are layer 2 switches.
NTP is enabled on all devices with 209.65.200.226 serving as the master clock source.
The client workstations receive their IP address and default gateway via R4’s DHCP server.
The default gateway address of 10.2.1.254 is the IP address of HSRP group 10 which is running
on DSW1 and DSW2.
In the IPv6 layer 3 topology R1, R2, and R3 are running OSPFv3 with an OSPF process number
6.
DSW1, DSW2 and R4 are running RIPng process name RIP_ZONE.
The two IPv6 routing domains, OSPF 6 and RIPng are connected via GRE tunnel running over the
underlying IPv4 OSPF domain. Redistrution is enabled where necessary.
Recently the implementation group has been using the test bed to do a ‘proof-of-concept’ on
several implementations. This involved changing the configuration on one or more of the devices.
You will be presented with a series of trouble tickets related to issues introduced during these
configurations.
Note: Although trouble tickets have many similar fault indications, each ticket has its own issue
and solution.
Each ticket has 3 sub questions that need to be answered & topology remains same.
Question-1Fault is found on which device,
Question-2Fault condition is related to,
Question-3What exact problem is seen & what needs to be done for solution
==================================================
Client is unable to ping IP 209.65.200.241
Solution
Steps need to follow as below:-When we check on client 1 & Client 2 desktop we are not receiving DHCP address from R4
Ipconfig —– Client will be receiving IP address 10.2.1.3
IP 10.2.1.3 will be able to ping from R4 , R3, R2 but not from R1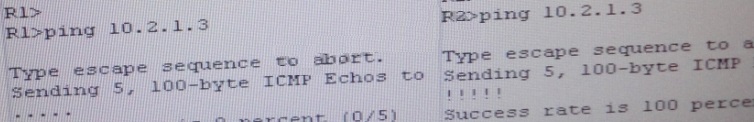
Check for neighborship of ospf
sh ip ospf nei —– Only one neighborship is forming with R2 & i.e. with R3
Since R2 is connected to R1 & R3 with routing protocol ospf than there should be 2 neighbors
seen but only one is seen
Need to check running config of R2 & R3 for interface
Sh run ————————– Interface Serial0/0/0/0.12 on R2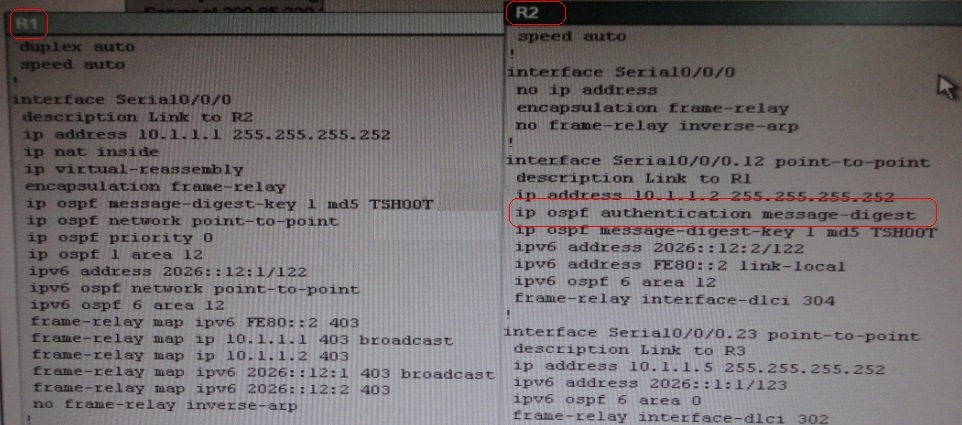
Sh run ————————– Interface Serial0/0/0/0 on R1
Change required:On R1, for IPV4 authentication of OSPF command is missing and required to
configure—— ip ospf authentication message-digest
—————————————————-
So in ticket Answer to the fault condition will be as below for:
The implementations group has been using the test bed to do a ‘proof-of-concept’ that
requires both Client 1 and Client 2 to access the WEB Server at 209.65.200.241. After
several changes to the network addressing, routing scheme, DHCP services, NTP services,
layer 2 connectivity, FHRP services, and device security, a trouble ticket has been opened
indicating that Client 1 cannot ping the 209.65.200.241 address.
Use the supported commands to isolated the cause of this fault and answer the following
questions.
On which device is the fault condition located?
which technology?
Topology Overview (Actual Troubleshooting lab design is for below network design)
Client Should have IP 10.2.1.3
EIGRP 100 is running between switch DSW1 & DSW2
OSPF (Process ID 1) is running between R1, R2, R3, R4
Network of OSPF is redistributed in EIGRP
BGP 65001 is configured on R1 with Webserver cloud AS 65002
HSRP is running between DSW1 & DSW2 Switches
The company has created the test bed shown in the layer 2 and layer 3 topology exhibits.
This network consists of four routers, two layer 3 switches and two layer 2 switches.
In the IPv4 layer 3 topology, R1, R2, R3, and R4 are running OSPF with an OSPF process
number 1.
DSW1, DSW2 and R4 are running EIGRP with an AS of 10. Redistribution is enabled where
necessary.
R1 is running a BGP AS with a number of 65001. This AS has an eBGP connection to AS 65002
in the ISP’s network. Because the company’s address space is in the private range.
R1 is also providing NAT translations between the inside (10.1.0.0/16 & 10.2.0.0/16) networks and
outside (209.65.0.0/24) network.
ASW1 and ASW2 are layer 2 switches.
NTP is enabled on all devices with 209.65.200.226 serving as the master clock source.
The client workstations receive their IP address and default gateway via R4’s DHCP server.
The default gateway address of 10.2.1.254 is the IP address of HSRP group 10 which is running
on DSW1 and DSW2.
In the IPv6 layer 3 topology R1, R2, and R3 are running OSPFv3 with an OSPF process number
6.
DSW1, DSW2 and R4 are running RIPng process name RIP_ZONE.
The two IPv6 routing domains, OSPF 6 and RIPng are connected via GRE tunnel running over the
underlying IPv4 OSPF domain. Redistrution is enabled where necessary.
Recently the implementation group has been using the test bed to do a ‘proof-of-concept’ on
several implementations. This involved changing the configuration on one or more of the devices.
You will be presented with a series of trouble tickets related to issues introduced during these
configurations.
Note: Although trouble tickets have many similar fault indications, each ticket has its own issue
and solution.
Each ticket has 3 sub questions that need to be answered & topology remains same.
Question-1Fault is found on which device,
Question-2Fault condition is related to,
Question-3What exact problem is seen & what needs to be done for solution
==================================================

Client is unable to ping IP 209.65.200.241
Solution
Steps need to follow as below:-When we check on client 1 & Client 2 desktop we are not receiving DHCP address from R4
Ipconfig —– Client will be receiving IP address 10.2.1.3
IP 10.2.1.3 will be able to ping from R4 , R3, R2 but not from R1
Check for neighborship of ospf
sh ip ospf nei —– Only one neighborship is forming with R2 & i.e. with R3
Since R2 is connected to R1 & R3 with routing protocol ospf than there should be 2 neighbors
seen but only one is seen
Need to check running config of R2 & R3 for interface
Sh run ————————– Interface Serial0/0/0/0.12 on R2
Sh run ————————– Interface Serial0/0/0/0 on R1
Change required:On R1, for IPV4 authentication of OSPF command is missing and required to
configure—— ip ospf authentication message-digest
—————————————————-
So in ticket Answer to the fault condition will be as below for:
The implementations group has been using the test bed to do a ‘proof-of-concept’ that
requires both Client 1 and Client 2 to access the WEB Server at 209.65.200.241. After
several changes to the network addressing, routing scheme, DHCP services, NTP services,
layer 2 connectivity, FHRP services, and device security, a trouble ticket has been opened
indicating that Client 1 cannot ping the 209.65.200.241 address.
Use the supported commands to isolated the cause of this fault and answer the following
questions.
The fault condition is related to which technology?
What is the solution to the fault condition?
Topology Overview (Actual Troubleshooting lab design is for below network design)
Client Should have IP 10.2.1.3
EIGRP 100 is running between switch DSW1 & DSW2
OSPF (Process ID 1) is running between R1, R2, R3, R4
Network of OSPF is redistributed in EIGRP
BGP 65001 is configured on R1 with Webserver cloud AS 65002
HSRP is running between DSW1 & DSW2 Switches
The company has created the test bed shown in the layer 2 and layer 3 topology exhibits.
This network consists of four routers, two layer 3 switches and two layer 2 switches.
In the IPv4 layer 3 topology, R1, R2, R3, and R4 are running OSPF with an OSPF process
number 1.
DSW1, DSW2 and R4 are running EIGRP with an AS of 10. Redistribution is enabled where
necessary.
R1 is running a BGP AS with a number of 65001. This AS has an eBGP connection to AS 65002
in the ISP’s network. Because the company’s address space is in the private range.
R1 is also providing NAT translations between the inside (10.1.0.0/16 & 10.2.0.0/16) networks and
outside (209.65.0.0/24) network.
ASW1 and ASW2 are layer 2 switches.
NTP is enabled on all devices with 209.65.200.226 serving as the master clock source.
The client workstations receive their IP address and default gateway via R4’s DHCP server.
The default gateway address of 10.2.1.254 is the IP address of HSRP group 10 which is running
on DSW1 and DSW2.
In the IPv6 layer 3 topology R1, R2, and R3 are running OSPFv3 with an OSPF process number
6.
DSW1, DSW2 and R4 are running RIPng process name RIP_ZONE.
The two IPv6 routing domains, OSPF 6 and RIPng are connected via GRE tunnel running over the
underlying IPv4 OSPF domain. Redistrution is enabled where necessary.
Recently the implementation group has been using the test bed to do a ‘proof-of-concept’ on
several implementations. This involved changing the configuration on one or more of the devices.
You will be presented with a series of trouble tickets related to issues introduced during these
configurations.
Note: Although trouble tickets have many similar fault indications, each ticket has its own issue
and solution.
Each ticket has 3 sub questions that need to be answered & topology remains same.
Question-1Fault is found on which device,
Question-2Fault condition is related to,
Question-3What exact problem is seen & what needs to be done for solution
==================================================

Client is unable to ping IP 209.65.200.241
Solution
Steps need to follow as below:-When we check on client 1 & Client 2 desktop we are not receiving DHCP address from R4
Ipconfig —– Client will be receiving IP address 10.2.1.3
IP 10.2.1.3 will be able to ping from R4 , R3, R2 but not from R1
Check for neighborship of ospf
sh ip ospf nei —– Only one neighborship is forming with R2 & i.e. with R3
Since R2 is connected to R1 & R3 with routing protocol ospf than there should be 2 neighbors
seen but only one is seen
Need to check running config of R2 & R3 for interface
Sh run ————————– Interface Serial0/0/0/0.12 on R2
Sh run ————————– Interface Serial0/0/0/0 on R1
Change required:On R1, for IPV4 authentication of OSPF command is missing and required to
configure—— ip ospf authentication message-digest
—————————————————-
So in ticket Answer to the fault condition will be as below for:
The implementations group has been using the test bed to do a ‘proof-of-concept’ that
requires both Client 1 and Client 2 to access the WEB Server at 209.65.200.241. After
several changes to the network addressing, routing scheme, DHCP services, NTP services,
layer 2 connectivity, FHRP services, and device security, a trouble ticket has been opened
indicating that Client 1 cannot ping the 209.65.200.241 address.
Use the supported commands to isolated the cause of this fault and answer the following
questions.
What is the solution to the fault condition?
which device is the fault condition located?
Topology Overview (Actual Troubleshooting lab design is for below network design)
Client Should have IP 10.2.1.3
EIGRP 100 is running between switch DSW1 & DSW2
OSPF (Process ID 1) is running between R1, R2, R3, R4
Network of OSPF is redistributed in EIGRP
BGP 65001 is configured on R1 with Webserver cloud AS 65002
HSRP is running between DSW1 & DSW2 Switches
The company has created the test bed shown in the layer 2 and layer 3 topology exhibits.
This network consists of four routers, two layer 3 switches and two layer 2 switches.
In the IPv4 layer 3 topology, R1, R2, R3, and R4 are running OSPF with an OSPF process
number 1.
DSW1, DSW2 and R4 are running EIGRP with an AS of 10. Redistribution is enabled where
necessary.
R1 is running a BGP AS with a number of 65001. This AS has an eBGP connection to AS 65002
in the ISP’s network. Because the company’s address space is in the private range.
R1 is also providing NAT translations between the inside (10.1.0.0/16 & 10.2.0.0/16) networks and
outside (209.65.0.0/24) network.
ASW1 and ASW2 are layer 2 switches.
NTP is enabled on all devices with 209.65.200.226 serving as the master clock source.
The client workstations receive their IP address and default gateway via R4’s DHCP server.
The default gateway address of 10.2.1.254 is the IP address of HSRP group 10 which is running
on DSW1 and DSW2.
In the IPv6 layer 3 topology R1, R2, and R3 are running OSPFv3 with an OSPF process number
6.
DSW1, DSW2 and R4 are running RIPng process name RIP_ZONE.
The two IPv6 routing domains, OSPF 6 and RIPng are connected via GRE tunnel running over the
underlying IPv4 OSPF domain. Redistrution is enabled where necessary.
Recently the implementation group has been using the test bed to do a ‘proof-of-concept’ on
several implementations. This involved changing the configuration on one or more of the devices.
You will be presented with a series of trouble tickets related to issues introduced during these
configurations.
Note: Although trouble tickets have many similar fault indications, each ticket has its own issue
and solution.
Each ticket has 3 sub questions that need to be answered & topology remains same.
Question-1Fault is found on which device,
Question-2Fault condition is related to,
Question-3What exact problem is seen & what needs to be done for solution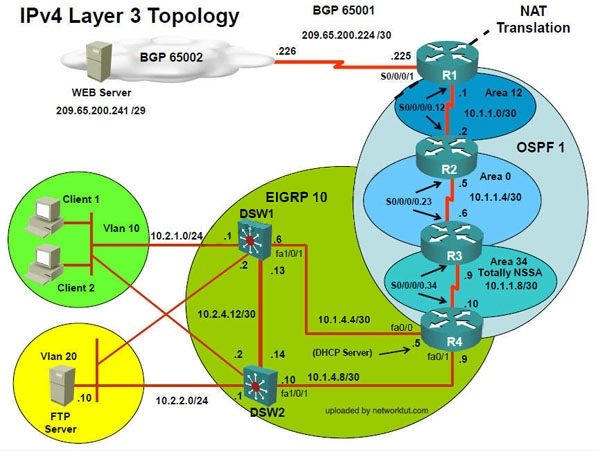
Client is unable to ping IP 209.65.200.241
Solution
Steps need to follow as below:-
When we check on client 1 & Client 2 desktop we are not receiving DHCP address from R4 ipconfig
Client will be receiving IP address 10.2.1.3
IP 10.2.1.3 will be able to ping from R4 , R3, R2, R1
Look for BGP Neighbourship
Sh ip bgp summary —– No O/P will be seen
Check for interface IP & ping IP 209.65.200.225
Reply will be received from Webserver
interface
Look for peering IP address via sh run on R1 interface serial 0/0/1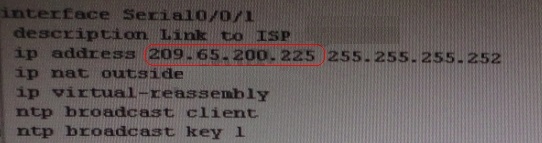
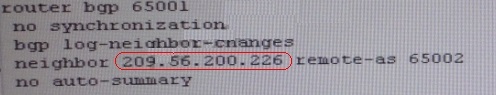
Since we are receiving icmp packets from Webserver interface on R1 so peering IP address
under router BGP is configured wrong IP but with correct AS nos.
Change required:On R1 under router BGP Change neighbor 209.56.200.226 remote-as 65002
statement to neighbor 209.65.200.226 remote-as 65002
—————————————————
So in ticket Answer to the fault condition will be as below for:
The implementations group has been using the test bed to do a ‘proof-of-concept’ that
requires both Client 1 and Client 2 to access the WEB Server at 209.65.200.241. After
several changes to the network addressing, routing schemes, DHCP services, NTP
services, layer 2 connectivity, FHRP services, and device security, a trouble ticket has been
opened indicating that Client 1 cannot ping the 209.65.200.241 address.
Use the supported commands to isolated the cause of this fault and answer the following
questions.
On which device is the fault condition located?
which technology?
Topology Overview (Actual Troubleshooting lab design is for below network design)
Client Should have IP 10.2.1.3
EIGRP 100 is running between switch DSW1 & DSW2
OSPF (Process ID 1) is running between R1, R2, R3, R4
Network of OSPF is redistributed in EIGRP
BGP 65001 is configured on R1 with Webserver cloud AS 65002
HSRP is running between DSW1 & DSW2 Switches
The company has created the test bed shown in the layer 2 and layer 3 topology exhibits.
This network consists of four routers, two layer 3 switches and two layer 2 switches.
In the IPv4 layer 3 topology, R1, R2, R3, and R4 are running OSPF with an OSPF process
number 1.
DSW1, DSW2 and R4 are running EIGRP with an AS of 10. Redistribution is enabled where
necessary.
R1 is running a BGP AS with a number of 65001. This AS has an eBGP connection to AS 65002
in the ISP’s network. Because the company’s address space is in the private range.
R1 is also providing NAT translations between the inside (10.1.0.0/16 & 10.2.0.0/16) networks and
outside (209.65.0.0/24) network.
ASW1 and ASW2 are layer 2 switches.
NTP is enabled on all devices with 209.65.200.226 serving as the master clock source.
The client workstations receive their IP address and default gateway via R4’s DHCP server.
The default gateway address of 10.2.1.254 is the IP address of HSRP group 10 which is running
on DSW1 and DSW2.
In the IPv6 layer 3 topology R1, R2, and R3 are running OSPFv3 with an OSPF process number
6.
DSW1, DSW2 and R4 are running RIPng process name RIP_ZONE.
The two IPv6 routing domains, OSPF 6 and RIPng are connected via GRE tunnel running over the
underlying IPv4 OSPF domain. Redistrution is enabled where necessary.
Recently the implementation group has been using the test bed to do a ‘proof-of-concept’ on
several implementations. This involved changing the configuration on one or more of the devices.
You will be presented with a series of trouble tickets related to issues introduced during these
configurations.
Note: Although trouble tickets have many similar fault indications, each ticket has its own issue
and solution.
Each ticket has 3 sub questions that need to be answered & topology remains same.
Question-1Fault is found on which device,
Question-2Fault condition is related to,
Question-3What exact problem is seen & what needs to be done for solution

Client is unable to ping IP 209.65.200.241
Solution
Steps need to follow as below:-
When we check on client 1 & Client 2 desktop we are not receiving DHCP address from R4 ipconfig
Client will be receiving IP address 10.2.1.3
IP 10.2.1.3 will be able to ping from R4 , R3, R2, R1
Look for BGP Neighbourship
Sh ip bgp summary —– No O/P will be seen
Check for interface IP & ping IP 209.65.200.225
Reply will be received from Webserver
interface
Look for peering IP address via sh run on R1 interface serial 0/0/1

Since we are receiving icmp packets from Webserver interface on R1 so peering IP address
under router BGP is configured wrong IP but with correct AS nos.
Change required:On R1 under router BGP Change neighbor 209.56.200.226 remote-as 65002
statement to neighbor 209.65.200.226 remote-as 65002
—————————————————
So in ticket Answer to the fault condition will be as below for:
The implementations group has been using the test bed to do a ‘proof-of-concept’ that
requires both Client 1 and Client 2 to access the WEB Server at 209.65.200.241. After
several changes to the network addressing, routing scheme, DHCP services, NTP services,
layer 2 connectivity, FHRP services, and device security, a trouble ticket has been opened
indicating that Client 1 cannot ping the 209.65.200.241 address.
Use the supported commands to isolated the cause of this fault and answer the following
questions.
The fault condition is related to which technology?
What is the solution to the fault condition?
Topology Overview (Actual Troubleshooting lab design is for below network design)
Client Should have IP 10.2.1.3
EIGRP 100 is running between switch DSW1 & DSW2
OSPF (Process ID 1) is running between R1, R2, R3, R4
Network of OSPF is redistributed in EIGRP
BGP 65001 is configured on R1 with Webserver cloud AS 65002
HSRP is running between DSW1 & DSW2 Switches
The company has created the test bed shown in the layer 2 and layer 3 topology exhibits.
This network consists of four routers, two layer 3 switches and two layer 2 switches.
In the IPv4 layer 3 topology, R1, R2, R3, and R4 are running OSPF with an OSPF process
number 1.
DSW1, DSW2 and R4 are running EIGRP with an AS of 10. Redistribution is enabled where
necessary.
R1 is running a BGP AS with a number of 65001. This AS has an eBGP connection to AS 65002
in the ISP’s network. Because the company’s address space is in the private range.
R1 is also providing NAT translations between the inside (10.1.0.0/16 & 10.2.0.0/16) networks and
outside (209.65.0.0/24) network.
ASW1 and ASW2 are layer 2 switches.
NTP is enabled on all devices with 209.65.200.226 serving as the master clock source.
The client workstations receive their IP address and default gateway via R4’s DHCP server.
The default gateway address of 10.2.1.254 is the IP address of HSRP group 10 which is running
on DSW1 and DSW2.
In the IPv6 layer 3 topology R1, R2, and R3 are running OSPFv3 with an OSPF process number
6.
DSW1, DSW2 and R4 are running RIPng process name RIP_ZONE.
The two IPv6 routing domains, OSPF 6 and RIPng are connected via GRE tunnel running over the
underlying IPv4 OSPF domain. Redistrution is enabled where necessary.
Recently the implementation group has been using the test bed to do a ‘proof-of-concept’ on
several implementations. This involved changing the configuration on one or more of the devices.
You will be presented with a series of trouble tickets related to issues introduced during these
configurations.
Note: Although trouble tickets have many similar fault indications, each ticket has its own issue
and solution.
Each ticket has 3 sub questions that need to be answered & topology remains same.
Question-1Fault is found on which device,
Question-2Fault condition is related to,
Question-3What exact problem is seen & what needs to be done for solution

Client is unable to ping IP 209.65.200.241
Solution
Steps need to follow as below:-
When we check on client 1 & Client 2 desktop we are not receiving DHCP address from R4 ipconfig
Client will be receiving IP address 10.2.1.3
IP 10.2.1.3 will be able to ping from R4 , R3, R2, R1
Look for BGP Neighbourship
Sh ip bgp summary —– No O/P will be seen
Check for interface IP & ping IP 209.65.200.225
Reply will be received from Webserver
interface
Look for peering IP address via sh run on R1 interface serial 0/0/1

Since we are receiving icmp packets from Webserver interface on R1 so peering IP address
under router BGP is configured wrong IP but with correct AS nos.
Change required:On R1 under router BGP Change neighbor 209.56.200.226 remote-as 65002
statement to neighbor 209.65.200.226 remote-as 65002
—————————————————
So in ticket Answer to the fault condition will be as below for:
The implementations group has been using the test bed to do a ‘proof-of-concept’ that
requires both Client 1 and Client 2 to access the WEB Server at 209.65.200.241. After
several changes to the network addressing, routing scheme, DHCP services, NTP services,
layer 2 connectivity, FHRP services, and device security, a trouble ticket has been opened
indicating that Client 1 cannot ping the 209.65.200.241 address.
Use the supported commands to isolated the cause of this fault and answer the following
questions.
What is the solution to the fault condition?
which device is the fault condition located?
Topology Overview (Actual Troubleshooting lab design is for below network design)
Client Should have IP 10.2.1.3
EIGRP 100 is running between switch DSW1 & DSW2
OSPF (Process ID 1) is running between R1, R2, R3, R4
Network of OSPF is redistributed in EIGRP
BGP 65001 is configured on R1 with Webserver cloud AS 65002
HSRP is running between DSW1 & DSW2 Switches
The company has created the test bed shown in the layer 2 and layer 3 topology exhibits.
This network consists of four routers, two layer 3 switches and two layer 2 switches.
In the IPv4 layer 3 topology, R1, R2, R3, and R4 are running OSPF with an OSPF process number 1.
DSW1, DSW2 and R4 are running EIGRP with an AS of 10. Redistribution is enabled where
necessary.
R1 is running a BGP AS with a number of 65001. This AS has an eBGP connection to AS 65002
in the ISP’s network. Because the company’s address space is in the private range.
R1 is also providing NAT translations between the inside (10.1.0.0/16 & 10.2.0.0/16) networks and
outside (209.65.0.0/24) network.
ASW1 and ASW2 are layer 2 switches.
NTP is enabled on all devices with 209.65.200.226 serving as the master clock source.
The client workstations receive their IP address and default gateway via R4’s DHCP server.
The default gateway address of 10.2.1.254 is the IP address of HSRP group 10 which is running
on DSW1 and DSW2.
In the IPv6 layer 3 topology R1, R2, and R3 are running OSPFv3 with an OSPF process number
6.
DSW1, DSW2 and R4 are running RIPng process name RIP_ZONE.
The two IPv6 routing domains, OSPF 6 and RIPng are connected via GRE tunnel running over the
underlying IPv4 OSPF domain. Redistrution is enabled where necessary.
Recently the implementation group has been using the test bed to do a ‘proof-of-concept’ on
several implementations. This involved changing the configuration on one or more of the devices.
You will be presented with a series of trouble tickets related to issues introduced during these
configurations.
Note: Although trouble tickets have many similar fault indications, each ticket has its own issue
and solution.
Each ticket has 3 sub questions that need to be answered & topology remains same.
Question-1Fault is found on which device,
Question-2Fault condition is related to,
Question-3What exact problem is seen & what needs to be done for solution
===========================================
Client is unable to ping IP 209.65.200.241
Solution
Steps need to follow as below:-
When we check on client 1 & Client 2 desktop we are not receiving DHCP address from R4
Ipconfig —– Client will be receiving IP address 10.2.1.3
IP 10.2.1.3 will be able to ping from R4 , R3, R2, R1
Look for BGP Neighbourship
Sh ip bgp summary —– State of BGP will be in established state & will be able to receive I prefix
(209.65.200.241)
As per troubleshooting we are able to ping ip 10.2.1.3 from R1 & BGP is also receiving prefix of
webserver & we are able to ping the same from R1. Further troubleshooting needs to be done
on R1 on serial 0/0/1
Check for running config. i.e sh run for interface serial 0/0/1..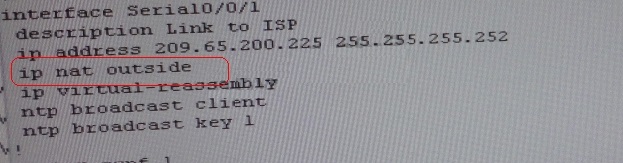
!
!
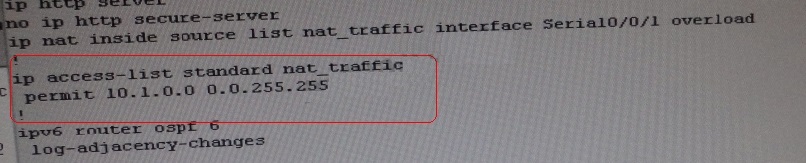
From above snapshot we are able to see that IP needs to be PAT to serial 0/0/1 to reach web
server IP
(209.65.200.241). But in access-list of NAT IP allowed IP is 10.1.0.0/16 is allowed & need 10.2.0.0
/16 to
As per troubleshooting we are able to ping ip 10.2.1.3 from R1 & BGP is also receiving prefix of
web server & we are able to ping the same from R1. Its should be checked further for running
config of interface for stopping
Change required:On R1, In natting we need to add client IP address for reachability to server.
————————————————–
So in ticket Answer to the fault condition will be as below for:
The implementations group has been using the test bed to do a ‘proof-of-concept’ that
requires both Client 1 and Client 2 to access the WEB Server at 209.65.200.241. After
several changes to the network addressing, routing schemes, DHCP services, NTP
services, layer 2 connectivity, FHRP services, and device security, a trouble ticket has been
opened indicating that Client 1 cannot ping the 209.65.200.241 address.
Use the supported commands to isolated the cause of this fault and answer the following
questions.
On which device is the fault condition located?
which technology?
Topology Overview (Actual Troubleshooting lab design is for below network design)
Client Should have IP 10.2.1.3
EIGRP 100 is running between switch DSW1 & DSW2
OSPF (Process ID 1) is running between R1, R2, R3, R4
Network of OSPF is redistributed in EIGRP
BGP 65001 is configured on R1 with Webserver cloud AS 65002
HSRP is running between DSW1 & DSW2 Switches
The company has created the test bed shown in the layer 2 and layer 3 topology exhibits.
This network consists of four routers, two layer 3 switches and two layer 2 switches.
In the IPv4 layer 3 topology, R1, R2, R3, and R4 are running OSPF with an OSPF process number 1.
DSW1, DSW2 and R4 are running EIGRP with an AS of 10. Redistribution is enabled where
necessary.
R1 is running a BGP AS with a number of 65001. This AS has an eBGP connection to AS 65002
in the ISP’s network. Because the company’s address space is in the private range.
R1 is also providing NAT translations between the inside (10.1.0.0/16 & 10.2.0.0/16) networks and
outside (209.65.0.0/24) network.
ASW1 and ASW2 are layer 2 switches.
NTP is enabled on all devices with 209.65.200.226 serving as the master clock source.
The client workstations receive their IP address and default gateway via R4’s DHCP server.
The default gateway address of 10.2.1.254 is the IP address of HSRP group 10 which is running
on DSW1 and DSW2.
In the IPv6 layer 3 topology R1, R2, and R3 are running OSPFv3 with an OSPF process number
6.
DSW1, DSW2 and R4 are running RIPng process name RIP_ZONE.
The two IPv6 routing domains, OSPF 6 and RIPng are connected via GRE tunnel running over the
underlying IPv4 OSPF domain. Redistrution is enabled where necessary.
Recently the implementation group has been using the test bed to do a ‘proof-of-concept’ on
several implementations. This involved changing the configuration on one or more of the devices.
You will be presented with a series of trouble tickets related to issues introduced during these
configurations.
Note: Although trouble tickets have many similar fault indications, each ticket has its own issue
and solution.
Each ticket has 3 sub questions that need to be answered & topology remains same.
Question-1Fault is found on which device,
Question-2Fault condition is related to,
Question-3What exact problem is seen & what needs to be done for solution
===========================================

Client is unable to ping IP 209.65.200.241
Solution
Steps need to follow as below:-
When we check on client 1 & Client 2 desktop we are not receiving DHCP address from R4
Ipconfig —– Client will be receiving IP address 10.2.1.3
IP 10.2.1.3 will be able to ping from R4 , R3, R2, R1
Look for BGP Neighbourship
Sh ip bgp summary —– State of BGP will be in established state & will be able to receive I prefix
(209.65.200.241)
As per troubleshooting we are able to ping ip 10.2.1.3 from R1 & BGP is also receiving prefix of
webserver & we are able to ping the same from R1. Further troubleshooting needs to be done
on R1 on serial 0/0/1
Check for running config. i.e sh run for interface serial 0/0/1..
!
!
From above snapshot we are able to see that IP needs to be PAT to serial 0/0/1 to reach web
server IP
(209.65.200.241). But in access-list of NAT IP allowed IP is 10.1.0.0/16 is allowed & need 10.2.0.0
/16 to
As per troubleshooting we are able to ping ip 10.2.1.3 from R1 & BGP is also receiving prefix of
web server & we are able to ping the same from R1. Its should be checked further for running
config of interface for stopping
Change required:On R1, In natting we need to add client IP address for reachability to server.
————————————————–
So in ticket Answer to the fault condition will be as below for:
The implementations group has been using the test bed to do a ‘proof-of-concept’ that
requires both Client 1 and Client 2 to access the WEB Server at 209.65.200.241. After
several changes to the network addressing, routing scheme, DHCP services, NTP services,
layer 2 connectivity, FHRP services, and device security, a trouble ticket has been opened
indicating that Client 1 cannot ping the 209.65.200.241 address.
Use the supported commands to isolated the cause of this fault and answer the following
questions.
The fault condition is related to which technology?

