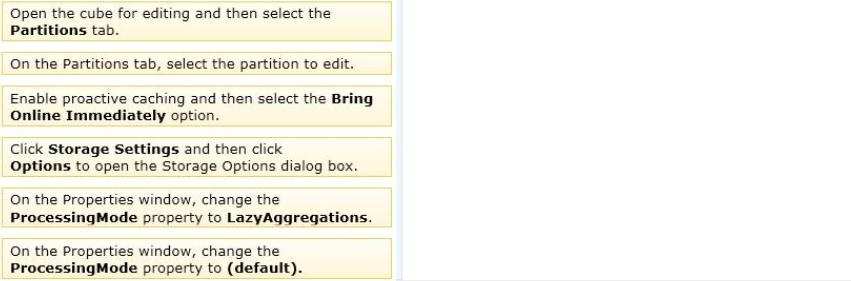
You are developing a SQL Server Analysis Services (SSAS) multidimensional project that is
configured to source data from a Microsoft Azure SQL Database database. The cube is processed
each night at midnight.
The largest partition in the cube takes 12 hours to process, and users are unable to access the
cube until noon. The partition must be available for querying as soon as possible after processing
commences.
You need to ensure that the partition is available for querying as soon as possible, without using
source data to satisfy the query.
Which three actions should you perform in sequence? (To answer, move the appropriate actions
from the list of actions to the answer area and arrange them in the correct order.)
Select and Place:

Explanation:
Note:
* Processing mode has two possible options.
Regular. This is the default setting. When set to regular, partitions will be available to users after
data has been loaded and aggregations are created completely.
Lazy Aggregations. When set to lazy aggregations, partitions will be available to user queries
immediately after data has been loaded. Aggregations will be created as a separate background
process while users start to query the partition.
* Lazy processing performs the task of building indexes and aggregations for dimensions and
measure group partitions at a lower priority to reduce foreground processing time and to allow
users to query the cube sooner. For lazy processing to occur, you must switch the
ProcessingMode = LazyAggregations of your measure group partitions; by default this value is
Regular (lazy processing is turned off). When processing a dimension with flexible aggregations
such as parent-child or virtual dimension by using the processing enumeration of ProcessUpdate
(such as to take into account of member name or hierarchy changes), lazy processing is initiated
to ensure that the aggregations are rebuilt on the associated measure group partitions.
* Configure Lazy Processing for the cube, measure group, or partition. If you configure Lazy
Processing, the dropped aggregations are recalculated as a background task. While the flexible
aggregations are being recalculated, users can continue to query the cube (without the benefit ofthe flexible aggregations). While the flexible aggregations are being recalculated, queries that
would benefit from the flexible aggregations run slower because Analysis Services resolves these
queries by scanning the fact data and then summarizing the data at query time. As the flexible
aggregations are recalculated, they become available incrementally on a partition-by-partition
basis. For a given cube, Lazy Processing is not enabled by default. You can configure it for a
cube, measure group, or partition by changing the ProcessingMode property from Regular to
LazyAggregations. To manage Lazy Processing, there are a series of server properties such as
the LazyProcessing \\ MaxObjectsInParallel setting, which controls the number of objects that can
be lazy processed at a given time. By default it is set to 2. By increasing this number, you increase
the number of objects processed in parallel; however, this also impacts query performance and
should therefore be handled with care.
* Incorrect: With Bring Online Immediately enabled, during cache refresh all queries are directed to
the relational source database to retrieve the latest data for end users. While this provides users
with refreshed data, it can also result in reduced query performance given that Analysis Services
needs to redirect queries to the relational source database.