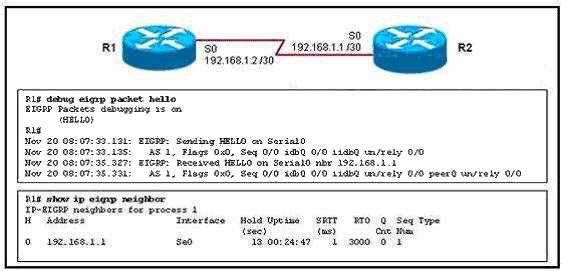
Routers R1 and R2 have established a neighbor relationship and are exchanging routing
information. The network design requires that R1 receive routing updates from R2, but not
advertise any routes to R2. Which configuration command sequence will successfully accomplish
this task?

A.
R1(config)# router eigrp 1
R1(config-router)# passive-interface serial 0
B.
R2(config)# router eigrp 1
R2(config-router)# passive-interface serial 0
C.
R1(config)# access-list 20 deny any
R1(config)# router eigrp 1
R1(config-router)# distribute-list 20 out serial 0
D.
R2(config)# access-list 20 deny any
R2(config)# router eigrp 1
R2(config-router)# distribute-list 20 out serial 0
E.
R1(config)# access-list 20 permit any
R1(config)# router eigrp 1
R1(config-router)# distribute-list 20 in serial 0
F.
R2(config)# access-list 20 permit any
R2(config)# router eigrp 1
R2(config-router)# distribute-list 20 in serial 0
Explanation:
We can not use passive-interfaces to accomplish this task because the “passive-interface…”
command (in EIGRP or OSPF) will shut down the neighbor relationship of these two routers (no
hello packets are exchanged). And to filter routing updates we should configure a distribute list on
R1 with an access list that deny all and apply it to the outbound direction so that R1 can receive
but cannot send routing updates.