What is the most likely cause of this?
Routers R1 and R2 are configured for HSRP as shown below:
Router R1:
interface ethernet 0
ip address 20.6.2.1 255.255.255.0
standby 35 ip 20.6.2.21
standby 35 priority 100
interface ethernet 1
ip address 20.6.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
standby 34 ip 20.6.1.21
Router R2:
interface ethernet 0
ip address 20.6.2.2 255.255.255.0
standby 35 ip 20.6.2.21
interface ethernet 1
ip address 20.6.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
standby 34 ip 20.6.1.21
standby 34 priority 100
You have configured the routers R1 & R2 with HSRP. While debugging router R2 you notice
very frequent HSRP group state transitions. What is the most likely cause of this?
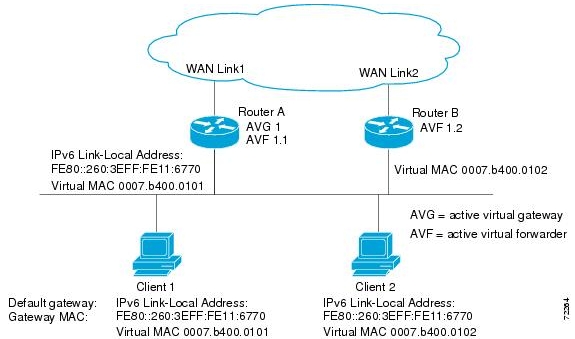
Which three statements accurately describe this GLBP topology?
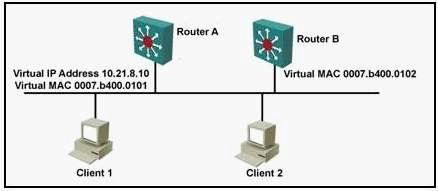
Which statement is true?
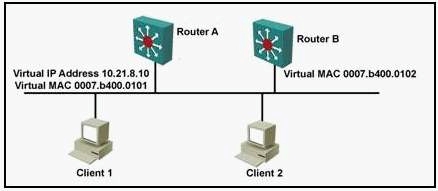
Which statement is true?
Which three WLAN statements are true?
Which three WLAN statements are true? (Choose three.)
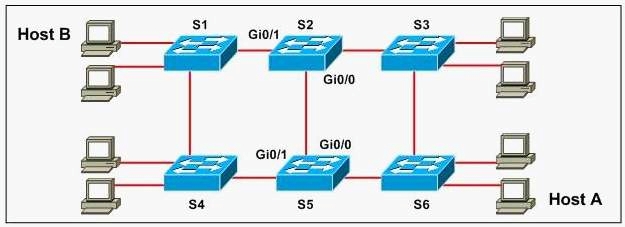
Will Host A be able to reach Host B?
which interfaces should root guard be configured to ensure that this happens?
Which two statements about the Cisco Aironet Desktop Utility (ADU) are true?
Which two statements about the Cisco Aironet Desktop Utility (ADU) are true? (Choose two.)
Which description correctly describes a MAC address flooding attack?
Which description correctly describes a MAC address flooding attack?
What is the condition of the adapter?
A Cisco Aironet Wireless LAN Adapter CB21AG is inserted into a PC cardbus slot. Both the
green status
LED and the amber activity LED are blinking slowly. What is the condition of the adapter?