What happens to packets that are forwarded from the 13.0.0.0/8 network to the Null0 interface?
Refer to the following.
Router # sh ip route eigrp
13.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
D 13.0.0.0/8 is a summary, 00:00:32, Null0
What happens to packets that are forwarded from the 13.0.0.0/8 network to the Null0
interface?
which state do DR and BDR establish adjacency with each OSPF router in the network?
In which state do DR and BDR establish adjacency with each OSPF router in the network?
what kind of topology?
A stub area is typically created using what kind of topology?
which two statements are true?
A network administrator is troubleshooting an EIGRP connection between RouterA, IP
address 10.1.2.1, and RouterB, IP address 10.1.2.2.
Given the debug output on RouterA, which two statements are true?
What command should be used to configure the spoke routers as EIGRP stub routers that will not advertise conne
Refer to the exhibit.
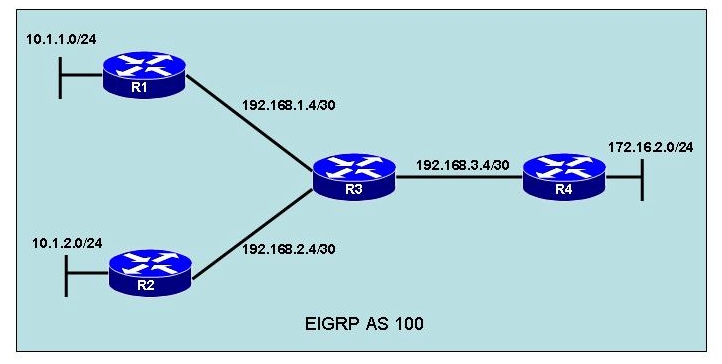
Network administrators have set up a hub and spoke topology with redundant connections
using EIGRP. However, they are concerned that a network outage between Router R1 and
Router R2 will cause traffic from the 10.1.1.x network to the 10.1.2.x network to traverse the
remote office links and overwhelm them. What command should be used to configure the
spoke routers as EIGRP stub routers that will not advertise connected networks, static
routes, or summary addresses?
what will EIGRP use to reach a destination?
If the primary path goes down, what will EIGRP use to reach a destination?
What command must the administrator issue to accomplish this?
A network administrator would like to configure an EIGRP router as a stub router that
advertises directly connected and summary routes only. What command must the
administrator issue to accomplish this?
What optional EIGRP configurations will be required in order to achieve full connectivity within AS 100?
Which two statements are EIGRP characteristics?
Which two statements are EIGRP characteristics? (Choose two.)