Which VPN management feature would be considered to ensure that the network had the least disruption of servic
Which VPN management feature would be considered to ensure that the network had the least disruption of service when making topology changes?
What type of Call Admission control in CallManager allows for limits to the bandwidth consumed by active calls
What type of Call Admission control in CallManager allows for limits to the bandwidth consumed by active calls?
Which one is not the feature of the Cisco Unified Wireless Network architecture?
Which one is not the feature of the Cisco Unified Wireless Network architecture?
What two choices can you make when redundancy is required from a branch office to a regional office? CareerCer
What two choices can you make when redundancy is required from a branch office to a regional office? CareerCert.blogspot.com
(Choose two.)
Which typical enterprise campus requirement ensures that the network supports the required applications and th
Which typical enterprise campus requirement ensures that the network supports the required applications and that data flows within the required time frames?
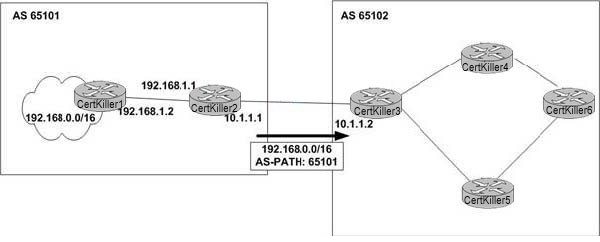
Which of the following statements about the BGP MED path attribute on Cisco routers is correct?
Which of the following statements about the BGP MED path attribute on Cisco routers is correct?
0/16 prefix to Domain 3 via BGP?
Based on the show ip route output in the exhibit, how can you tell if a BGP route is learned via IBGP or EBGP?
Exhibit:
Domain router#show ip route
Codes: C – connected, S – static, I – IGRP, R – RIP, M – mobile, B – BGP
D – EIGRP, EX – EIGRP external, O – OSPF, IA – OSPF inter area
N1 – OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 – OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 – OSPF external type 1, E2 – OSPF external type 2, EEGP i – IS-IS, L1 – IS-IS level-1, L2 – IS-IS level-2, * -candidate default
U – per-user static route, o – ODR
T – traffic engineered route
Gateway of last resort is not set
172.16.0.0/24 is subnetted, 2 subnets
B 172.16.10.0 [20/0] via 10.1.1.100, 00:00:24
B 172.16.11.0 [20/0] via 10.1.1.100, 00:00:24
172.26.0.0/28 is subnetted, 3 subnets
B 172.26.1.48 [200/0] via 192.168.1.50, 00:00:31
B 172.26.1.32 [200/0] via 192.168.1.50, 00:00:31
B 172.26.1.16 [200/0] via 192.168.1.50, 00:00:31
10.0.0.0/8 is variable subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
B 10.0.0/8 [20/0] via 10.1.1.100, 00:00:24
C 10.1.1.0/24 is directly connected, Serial3
192.168.1.0/28 is subnetted, 3 subnets
C 192.168.1.32 is directly connected, Serial1
C 192.168.1.48 is directly connected, Serial2
C 192.168.1.16 is directly connected, Serial0
192.168.2.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
B 192.168.2.64/28 [20/0] via 10.1.1.100, 00:00:26
Based on the show ip route output in the exhibit, how can you tell if a BGP route is learned via IBGP or EBGP?
What is step 2?
BGP table
Address Prefix AS-Path Next hop Communities Other attr.
10.0.0.0 /8 65100 65101 1.1.1.1 65101:111
… … … … … …
IP routing table
Protocol Address Prefix Next-hop Outgoing interface BGP 10.0.0.0 /8 1.1.1.1
OSPF 1.1.1.1 /32 172.16.1.2 Ethernet 0
conn. 172.16.1.0 /24 Ethernet 0
IP routing table
Protocol Address Prefix Next-hop Outgoing
interface
BGP 10.0.0.0 /8 1.1.1.1
OSPF 1.1.1.1 /32 172.16.1.2 Ethernet 0
conn. 172.16.1.0 /24 Ethernet 0
To forward a packet to 10.0.0.0/8, the router perform the following steps:
Step 1. Search the ip routing table for a route to reach the 10.0.0.0/8 network.
Step 2. ___________________________
Step 3. Find the connected outgoing interface to reach 172.16.1.2. Step 4. Arp for the 172.16.1.2 MAC address if it is not already in the ARP cache. Step 5. Store the 172.16.1.2 MAC address in the Fast Switching cache for successive packets to network 10.0.0.0.
What is step 2?