What describes a landing zone in a disk drive?

A.
Area on which the read/write head rests
B.
Area where the read/write head lands to access data
C.
Area where the data is buffered before writing to platters
D.
Area where sector-specific information is stored on the disk
Explanation:
The key components of a hard disk drive are platter, spindle, read-write head, actuator arm
assembly, and controller board. I/O operations in a HDD is performed by rapidly moving the arm
across the rotating flat platters coated with magnetic particles. Data is transferred between the
disk controller and magnetic platters through the read-write (R/W) head which is attached to the
arm. Data can be recorded and erased on magnetic platters any number of times.
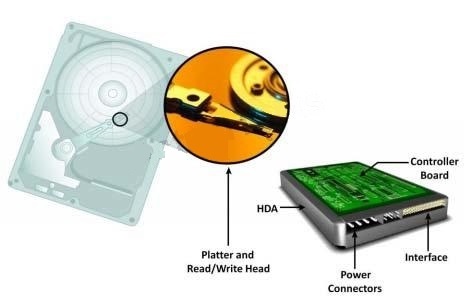
Platter: A typical HDD consists of one or more flat circular disks called platters. The data is
recorded on these platters in binary codes (0s and 1s). The set of rotating platters is sealed in a
case, called Head Disk Assembly (HDA). A platter is a rigid, round disk coated with magnetic
material on both surfaces (top and bottom). The data is encoded by polarizing the magnetic area,
or domains, of the disk surface. Data can be written to or read from both surfaces of the platter.
The number of platters and the storage capacity of each platter determine the total capacity of the
drive.
Spindle: A spindle connects all the platters and is connected to a motor. The motor of the spindle
rotates with a constant speed. The disk platter spins at a speed of several thousands of
revolutions per minute (rpm). Common spindle speeds are 5,400 rpm, 7,200 rpm, 10,000 rpm, and
15,000 rpm. The speed of the platter is increasing with improvements in technology; although, the
extent to which it can be improved is limited.
Read/Write Head: Read/Write (R/W) heads, read and write data from or to platters. Drives have
two R/W heads per platter, one for each surface of the platter. The R/W head changes the agnetic
polarization on the surface of the platter when writing data. While reading data, the head detects
the magnetic polarization on the surface of the platter. During reads and writes, the R/W head
senses the magnetic polarization and never touches the surface of the platter. When the spindle isrotating, there is a microscopic air gap maintained between the R/W heads and the platters,
known as the head flying height. This air gap is removed when the spindle stops rotating and the
R/W head rests on a special area on the platter near the spindle. This area is called the landing
zone . The landing zone is coated with a lubricant to reduce friction between the head and the
platter. The logic on the disk drive ensures that heads are moved to the landing zone before they
touch the surface. If the drive malfunctions and the R/W head accidentally touches the surface of
the platter outside the landing zone, a head crash occurs. In a head crash, the magnetic coating
on the platter is scratched and may cause damage to the R/W head. A head crash generally
results in data loss.
Actuator Arm Assembly: R/W heads are mounted on the actuator arm assembly, which positions
the R/W head at the location on the platter where the data needs to be written or read. The R/W
heads for all platters on a drive are attached to one actuator arm assembly and move across the
platters simultaneously.
Drive Controller Board: The controller is a printed circuit board, mounted at the bottom of a disk
drive. It consists of a microprocessor, internal memory, circuitry, and firmware. The firmware
controls the power to the spindle motor and the speed of the motor. It also manages the
communication between the drive and the host. In addition, it controls the R/W operations by
moving the actuator arm and switching between different R/W heads, and performs the
optimization of data access.


A
0
0