DRAG DROP
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that use the same scenario. For your convenience,
the scenario is repeated in each question. Each question presents a different goal and answer choices,
but the text of the scenario is exactly the same in each question in this series.
Start of repeated scenario
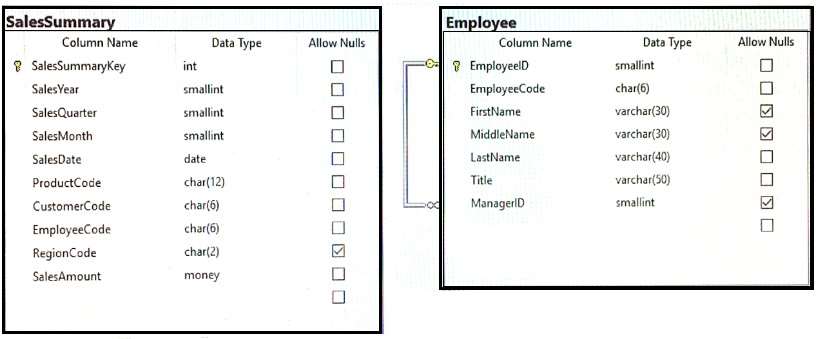
You have a database that contains the tables shown in the exhibit. (Click the Exhibit button.)
You review the Employee table and make the following observations:Every record has a value in the ManagerID except for the Chief Executive Officer (CEO).
The FirstName and MiddleName columns contain null values for some records.
The valid values for the Title column are Sales Representative manager, and CEO.
You review the SalesSummary table and make the following observations:
The ProductCode column contains two parts: The first five digits represent a product code, and the last
seven digits represent the unit price. The unit price uses the following pattern: ####.##.
You observe that for many records, the unit price portion of the ProductCode column contains values.
The RegionCode column contains NULL for some records.
Sales data is only recorded for sales representatives.
You are developing a series of reports and procedures to support the business. Details for each report or
procedure follow.
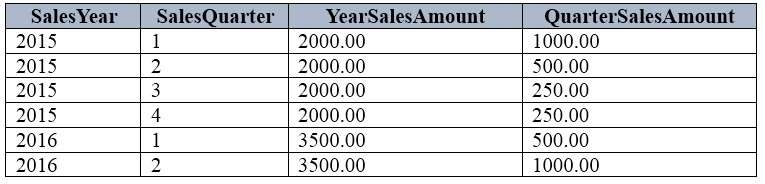
Sales Summary report: This report aggregates data by year and quarter. The report must resemble the
following table.
Sales Manager report: This report lists each sales manager and the total sales amount for all employees that
report to the sales manager.
Sales by Region report: This report lists the total sales amount by employee and by region. The report must
include the following columns: EmployeeCode, MiddleName, LastName, RegionCode, and SalesAmount. If
MiddleName is NULL, FirstName must be displayed. If both FirstName and MiddleName have null values, the
world Unknown must be displayed/ If RegionCode is NULL, the word Unknown must be displayed.
Report1: This report joins data from SalesSummary with the Employee table and other tables. You plan to
create an object to support Report1. The object has the following requirements:
be joinable with the SELECT statement that supplies data for the report
can be used multiple times with the SELECT statement for the report
be usable only with the SELECT statement for the report
not be saved as a permanent object
Report2: This report joins data from SalesSummary with the Employee table and other tables.
You plan to create an object to support Report1. The object has the following requirements:
be joinable with the SELECT statement that supplies data for the report
can be used multiple times for this report and other reports
accept parameters
be saved as a permanent object
Sales Hierarchy report: This report aggregates rows, creates subtotal rows, and super-aggregates rows over
the SalesAmount column in a single result-set. The report uses SaleYear, SaleQuarter, and SaleMonth as a
hierarchy. The result set must not contain a grand total or cross-tabulation aggregate rows.
Current Price Stored Procedure: This stored procedure must return the unit price for a product when a product
code is supplied. The unit price must include a dollar sign at the beginning. In addition, the unit price mustcontain a comma every three digits to the left of the decimal point, and must display two digits to the left of the
decimal point. The stored procedure must not throw errors, even if the product code contains invalid data.
End of Repeated Scenario
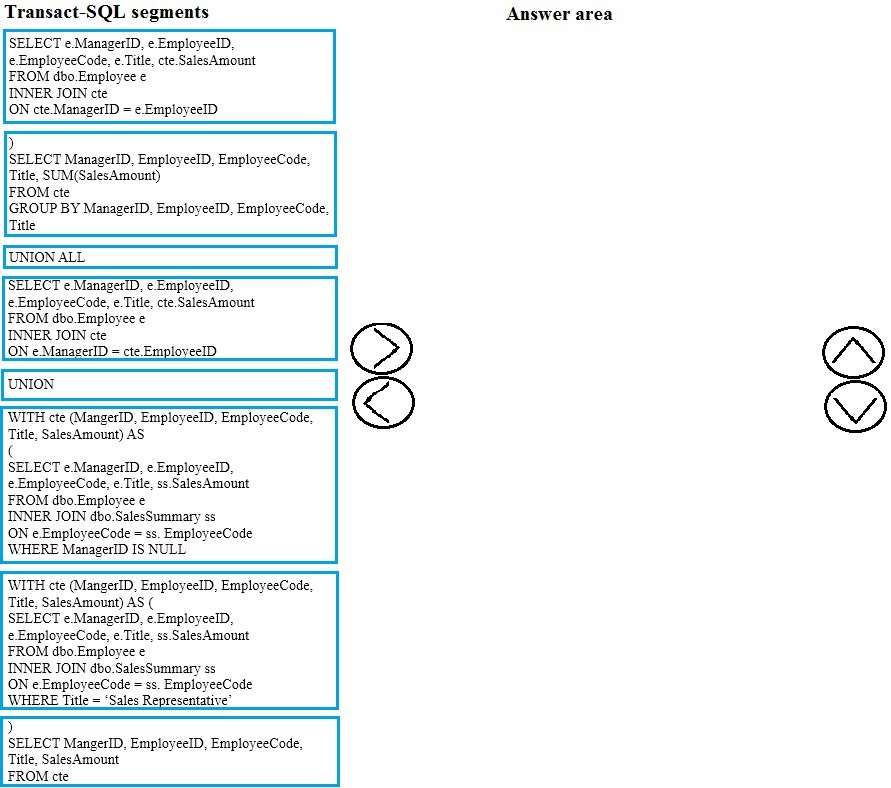
You need to create the query for the Sales Managers report.
Which four Transact-SQL segments should you use to develop the solution? To answer, move the appropriate
Transact-SQL segments from the list of Transact-SQL segments to the answer area and arrange them in the
correct order.
Select and Place:

Explanation:
From scenario: Sales Manager report: This report lists each sales manager and the total sales amount for
allemployees that report to the sales manager.
Box 1:..WHERE Title=’Sales representative’
The valid values for the Title column are Sales Representative manager, and CEO.
First we define the CTE expression.
Note: A common table expression (CTE) can be thought of as a temporary result set that is defined within the
execution scope of a single SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, or CREATE VIEW statement. A CTE is
similar to a derived table in that it is not stored as an object and lasts only for the duration of the query. Unlike a
derived table, a CTE can be self-referencing and can be referenced multiple times in the same query.
Box 2:
Use the CTE expression one time.
Box 3: UNION
Box 4:
Use the CTE expression a second time.
https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms190766(v=sql.105).aspx



USING UNION WILL PUT THE RESULT IN DESCENDING however UNION ALL will ascend them so it might be UNION ALL as the view is a bit more clearer
0
7
on cte.ManagerId = e.EmployeeId
2
0
Confirmed using SQL Management Studio
with cte (mangerId,employeeId,amount)
as (
select e.mangerId, e.employeeId, ss.amount
from Employee e inner join Sales ss
on e.EmployeeId = ss.EmployeeId)
select mangerId,employeeId,sum(amount)
from cte
group by mangerId,employeeId
union all
select e.mangerId,e.employeeId,cte.amount
from Employee e
inner join cte
on cte.MangerId = e.EmployeeId
1
1
the answer is correct
2
11
AS this is for the Sales Manager Report and according to the requirements for it, Common Table Expression is applied here:
WITH CTE (ManagerID, SalesAmount) AS (
SELECT E.ManagerID, S.SalesAmount
FROM Employee AS E
INNER JOIN SalesSummary AS S
ON E.EmployeeCode = S.EmployeeCode
WHERE Title = ‘Sales Representative’
)
SELECT ManagerID, SUM(SalesAmount)
FROM CTE
GROUP BY ManagerID
1
2
Sorry the previous reply is probably not correct because there might be a multi-level hierarchy. In such case, the recursive form of CTE should be applied:
WITH CTE (ManagerID, SalesAmount) AS
(
SELECT E.ManagerID, S.SalesAmount
FROM Employee AS E
INNER JOIN SalesSummary AS S
ON E.EmployeeCode = S.EmployeeCode
WHERE Title = ‘Sales Representative’
UNION ALL
SELECT M.ManagerID, C.SalesAmount
FROM Employee AS M
INNER JOIN CTE AS C
ON M.EmployeeID = C.ManagerID
)
SELECT ManagerID, SUM(SalesAmount)
FROM CTE
GROUP BY ManagerID
2
1
Final correction to my solution as the Anchor Member in the CTE should return just a result:
WITH cte (ManagerID, EmployeeID, EmployeeCode, Title, SalesAmount) AS
(
SELECT e.ManagerID, e.EmployeeID, e.EmployeeCode, e.Title, ss.SalesAmount
FROM dbo.Employee e
INNER JOIN dbo.SalesSummary ss
ON e.EmployeeCode = ss.EmployeeCode
WHERE ManagerID IS NULL
UNION ALL
SELECT e.ManagerID, e.EmployeeID, e.EmployeeCode, e.Title, cte.SalesAmount
FROM dbo.Employee e
INNER JOIN cte
ON e.ManagerID = cte.EmployeeID
)
SELECT ManagerID, EmployeeID, EmployeeCode, Title, SUM(SalesAmount)
FROM cte
GROUP BY ManagerID, EmployeeID, EmployeeCode, Title
5
0
Here is the answer:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/t-sql/queries/with-common-table-expression-transact-sql?view=sql-server-2017
1
0
I don’t know why does all the answers above are using Hierarchy in this question. Let’s extract valuable information from the Question First:
– Question is : You need to create the query for the Sales Managers report.
Which four Transact-SQL segments should you use to develop the solution?
– Supportive information about Sales Manager report is:
Sales Manager report: This report lists each sales manager and the total sales amount for all employees that report to the sales manager.
The valid values for the Title column are Sales Representative manager, and CEO.
According to the given information, the result table should only include sales manager and sales representative report to them. So the answer should be
WITH CTE (ManagerID, SalesAmount) AS (
SELECT E.ManagerID, S.SalesAmount
FROM Employee AS E
INNER JOIN SalesSummary AS S
ON E.EmployeeCode = S.EmployeeCode
WHERE Title = ‘Sales Representative’
)
SELECT ManagerID, EmployeeID, EmployeeCode, Title, SUM(SalesAmount)
FROM CTE
GROUP BY ManagerID, EmployeeID, EmployeeCode, Title
0
1