Which of the following SELECT statement would you write?
You work as a database administrator at ABC.com. ABC.com has a SQL Server 2012 database
named ProductsDB. The relevant part of the ProductsDB is shown in the following database
diagram: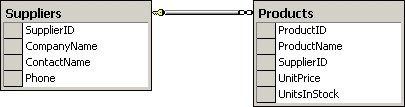
You need to write a Transact-SQL query that display a single row in the following XML format:
<row ProductID=”1001″ Product=”Product Name”, Price=”24.99″ InStock=”16″
Supplier=”Company Name” Contact=”Contact Name” Phone=”346 959 2215″ />
Which of the following SELECT statement would you write?
Which of the following SELECT statement would you write?
You work as a database administrator at ABC.com. ABC.com has a SQL Server 2012 database
named SalesDB. The SalesDB is shown in the following database diagram: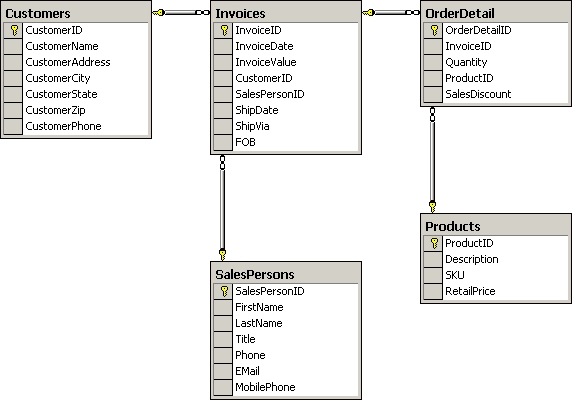
You need to write a Transact-SQL query that display a single row in the following XML format:
<Invoices InvoiceID=”1001″ Date=”2012-10-01T00:00:00″, Value=”1000.00″ Customer=”Customer
Name” ShippedTo=”Customer City” />
Which of the following SELECT statement would you write?
Which of the following SELECT statement would you write?
You work as a database administrator at ABC.com. ABC.com has a SQL Server 2012 database
named ProductsDB. The ProductsDB database is shown in the following database diagram: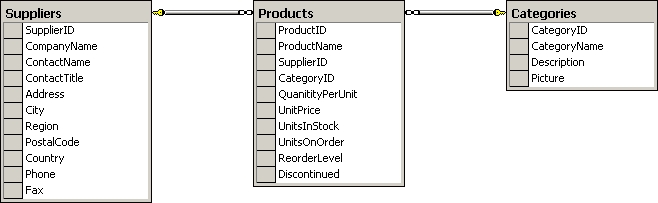
You need to write a Transact-SQL query that displays all the products received by a single
supplier in the following XML format:
<Suppliers SupplierID=”22″ Company=”Company Name” ContactNumber=”510 250 6400″>
<Products ProductID=”100″ UnitPrice=”249.00″ UnitsInStock=”7″ />
<Products ProductID=”118″ UnitPrice=”559.00″ UnitsInStock=”12″ />
</Suppliers>
Which of the following SELECT statement would you write?
Which of the following SELECT statement would you use?
CORRECT TEXT
You work as a SQL Server 2012 database developer at ABC.com. You are developing a query for
a database driven Web application that allows visitors to vote for the cricket player of the week.
The number of votes is stored in a table named WeeklyVotes that has columns named Week,
PlayerName, Votes.
You need to write a Transact-SQL query that ranks the top 30 cricket players by the average votes
over the last 12 months. You want the top 10 cricket players to have a rank of 1, the next 10 to
have a rank of 2, and the last 10 to have a rank of 3.
Which of the following SELECT statement would you use?
To answer, type the correct code in the answer area.
Which ranking function should you use?
You work as a database developer at ABC.com. ABC.com has a SQL Server 2012 database
named SalesDB that has a table named WeeklySales. The WeeklySales table records the sales
amount for each of ABC.com’s 20 sales representitives.
You need to write a Transact-SQL query that ranks the sales representatives by the average sales
amount for the past year. You want the sales representatives with the same average sales amount
to have the same rank with the subsequent rank being skipped.
Which ranking function should you use?
Which of the following SELECT statement would accomplish this task?
You work as a SQL Server 2012 database developer at ABC.com. You are developing a query for
a database driven Web application that allows visitors to vote for the cricket player of the week.
The number of votes is stored in a table named WeeklyVotes that has columns named Week,
PlayerName, Votes.
You need to write a Transact-SQL query that returns the cricket player that received the most
votes for each week, as well as the number of votes they received.
Which of the following SELECT statement would accomplish this task?
What Transact-SQL statements would accomplish this task?
You work as a database developer at ABC.com. ABC.com has a SQL Server 2012 database
named SalesDB that has a table named Inventory.
The Inventory table has three columns named ProductID, InStore and InWarehouse. The
ProductID column is the primary key and is linked to the Products table. The InStore column
stores the quantity of a product that is held at ABC.com’s retail shop, while the InWarehouse
column stores the quantity of a product that is held at ABC.com’s warehouse.
You need to add a computed column that stores the total number of a product that ABC.com has.
What Transact-SQL statements would accomplish this task?
Which of the following statements should you use in the trigger definition?
ABC.com has a SQL Server 2012 database instance that hosts a database named ComDB. The
ComDB database has a table named Partners that was created using the following Transact-SQL
code:
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[Partners]
(
[CompanyID] [int] NOT NULL,
[CompanyName] [nvarchar] (50) NOT NULL,
[Location] [nvarchar] (50) NOT NULL,
[ContactName] [nvarchar] (50) NOT NULL,
[Email] [nvarchar] (50) NOT NULL,
[Phone] [nvarchar] (10) NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT [PK_Partners] PRIMARY KEY CLUSTERED
(
[CompanyID] ASC
)
ON PRIMARY
)
You want to create a FOR UPDATE trigger that will track changes to the ContactName and Phone
columns.
Which of the following statements should you use in the trigger definition?
How should you configure the view to ensure optimal performance?
You are the database administrator of a SQL Server 2012 database infrastructure at ABC.com.
You need to optimize a very large database table that contains several million rows of data by
designing a view based on the table. The view must allow users to perform aggregations on
several columns.
How should you configure the view to ensure optimal performance?
How would you guarantee that values in the Events.CompanyID column already exist in the Partners.CompanyID col
You are the database developer at ABC.com. ABC.com has a SQL Server 2012 database
infrastructure that has a database named ComDB with a table named Partners.
The Partners table was created using the following Transact-SQL code:
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[Partners]
(
[CompanyID] [int] NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY,
[CompanyName] [varchar] (150) NOT NULL,
[Location] [varchar] (150) NOT NULL,
[ContactName] [varchar] (150) NOT NULL,
[Email] [varchar] (150) NOT NULL,
[Phone] [varchar] (10) NOT NULL
)
You develop a new table named Events using the following Transact-SQL code:
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[Events]
(
[EventID] [int] NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY,
[CompanyID] [int] NOT NULL,
[EventDescription] [varchar] (2500),
[EventCordinator] [varchar] (150) NOT NULL
)
How would you guarantee that values in the Events.CompanyID column already exist in the
Partners.CompanyID column?

