You need to ensure that users can send and receive encrypted email messages using S/MIME.
You have an Exchange organization. All servers in the organization have Exchange Server 2010 SP1 installed.
The network contains an internal root certification authority (CA).
Users on the network use Outlook Anywhere. A Client Access server uses a wildcard certificate issued by a trusted third-party root CA.
You need to ensure that users can send and receive encrypted email messages using S/MIME.
What should you do?
What should you create for User1?
You have an Exchange organization. All servers in the organization have Exchange Server 2010 SP1 installed.
All users use Microsoft Outlook 2010.
A user named User1 reaches her mailbox size limit.
You need to ensure that User1 can archive email messages located in her mailbox and read the archived messages when she works offline.
What should you create for User1?
You need to add a default policy tag to a retention policy
You have an Exchange organization. All servers in the organization have Exchange Server 2010 SP1 installed.
You create a retention policy and apply the policy to all of the mailboxes in the organization.
You need to add a default policy tag to a retention policy. The tag must move all email messages automatically to a Personal Archive six months after the messages are received.
What should you do first?
You need to ensure that users can use personal tags that are not linked to the retention policy.
You have an Exchange organization. All servers in the organization have Exchange Server 2010 SP1 installed.
You create a retention policy and apply the policy to all of the mailboxes in the organization.
You need to ensure that users can use personal tags that are not linked to the retention policy.
What should you do?
You need to install the Exchange Server 2010 SP1 pre-requisites for the Mailbox, Client Access, and Hub Transp
You have a server that runs Windows Server 2008 SP2. You plan to install Exchange Server 2010 SP1 on the server.
You need to install the Exchange Server 2010 SP1 pre-requisites for the Mailbox, Client Access, and Hub Transport server roles.
What should you do from the server?
You need to ensure that you can modify the default email address policy by using the Exchange Management Conso
You have an Exchange Server 2003 organization.
You install a new Exchange Server 2010 SP1 server in the organization.
You need to ensure that you can modify the default email address policy by using the Exchange Management Console (EMC).
What should you do?
Which role should you identify?
You plan to install Exchange Server 2010 SP1 servers in an existing Exchange Server 2007 organization. All servers will co-exist in a single Active Directory site.
You need to identify which role must be transitioned to Exchange Server 2010 first.
Which role should you identify?
You need to prepare the Exchange organization for the deployment of Exchange Server 2010 Mailbox, Client Acces
You have an Exchange organization that contains Exchange Server 2003 SP2 servers. All servers are members of one Administrative Group and one Routing Group.
You plan to transition the organization to a hosted Exchange Server 2010 environment.
You need to prepare the Exchange organization for the deployment of Exchange Server 2010 Mailbox, Client Access and Hub Transport servers.
What should you do first?
Which cmdlet should you run?
You have an Exchange Server 2010 SP1 server that hosts a public folder database named PUBLIC.
You need to move the transaction log files of PUBLIC.
Which cmdlet should you run?
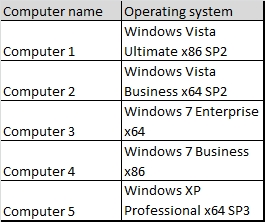
Which two computers should you identify? (Each correct answer presents part of the solution
You have an Exchange Server 2010 organization.
The network contains the computers shown in the following table:
You need to identify which computers can run Exchange Server 2010 SP1 management tools.
Which two computers should you identify? (Each correct answer presents part of the solution. Choose two).