You need to create the Sales Order table How should you…
HOTSPOT
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that use the same scenario. For your convenience, the
scenario is repeated in each question. Each question presents a different goal and answer choices, but the text
of the scenario is exactly the same in each question in this series.
You have a database that contains the following tables: BlogCategory, BlogEntry, ProductReview, Product, and
SalesPerson. The tables were created using the following Transact SQL statements:
You must modify the ProductReview Table to meet the following requirements:
1. The table must reference the ProductID column in the Product table
2. Existing records in the ProductReview table must not be validated with the Product table.
3. Deleting records in the Product table must not be allowed if records are referenced by the ProductReview
table.
4. Changes to records in the Product table must propagate to the ProductReview table.
You also have the following databse tables: Order, ProductTypes, and SalesHistory, The transact-SQL
statements for these tables are not available.
You must modify the Orders table to meet the following requirements:
1. Create new rows in the table without granting INSERT permissions to the table.
2. Notify the sales person who places an order whether or not the order was completed.
You must add the following constraints to the SalesHistory table:
– a constraint on the SaleID column that allows the field to be used as a record identifier
– a constant that uses the ProductID column to reference the Product column of the ProductTypes table
– a constraint on the CategoryID column that allows one row with a null value in the column
– a constraint that limits the SalePrice column to values greater than four
Finance department users must be able to retrieve data from the SalesHistory table for sales persons wherethe value of the SalesYTD column is above a certain threshold.
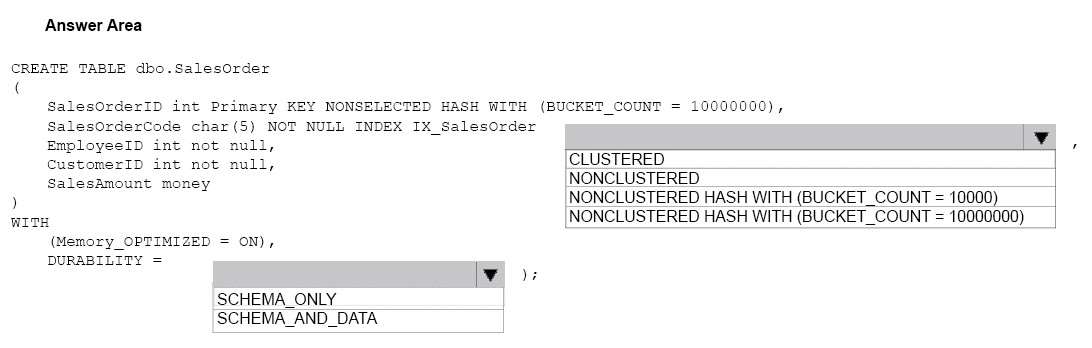
You plan to create a memory-optimized table named SalesOrder. The table must meet the following
requirments:
– The table must hold 10 million unique sales orders.
– The table must use checkpoints to minimize I/O operations and must not use transaction logging.
– Data loss is acceptable.
Performance for queries against the SalesOrder table that use Where clauses with exact equality operations
must be optimized.
You need to create the Sales Order table
How should you complete the table definition? To answer? select the appropriate Transact-SQL segments in
the answer area.
Hot Area:
How should you complete the procedure?
HOTSPOT
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that use the same scenario. For your convenience, the
scenario is repeated in each question. Each question presents a different goal and answer choices, but the text
of the scenario is exactly the same in each question in this series.
You have a database that contains the following tables: BlogCategory, BlogEntry, ProductReview, Product, and
SalesPerson. The tables were created using the following Transact SQL statements:
You must modify the ProductReview Table to meet the following requirements:
1. The table must reference the ProductID column in the Product table
2. Existing records in the ProductReview table must not be validated with the Product table.
3. Deleting records in the Product table must not be allowed if records are referenced by the ProductReview
table.
4. Changes to records in the Product table must propagate to the ProductReview table.
You also have the following databse tables: Order, ProductTypes, and SalesHistory, The transact-SQL
statements for these tables are not available.
You must modify the Orders table to meet the following requirements:
1. Create new rows in the table without granting INSERT permissions to the table.
2. Notify the sales person who places an order whether or not the order was completed.
You must add the following constraints to the SalesHistory table:
– a constraint on the SaleID column that allows the field to be used as a record identifier
– a constant that uses the ProductID column to reference the Product column of the ProductTypes table
– a constraint on the CategoryID column that allows one row with a null value in the column
– a constraint that limits the SalePrice column to values greater than four
Finance department users must be able to retrieve data from the SalesHistory table for sales persons wherethe value of the SalesYTD column is above a certain threshold.
You plan to create a memory-optimized table named SalesOrder. The table must meet the following
requirments:
– The table must hold 10 million unique sales orders.
– The table must use checkpoints to minimize I/O operations and must not use transaction logging.
– Data loss is acceptable.
Performance for queries against the SalesOrder table that use Where clauses with exact equality operations
must be optimized.
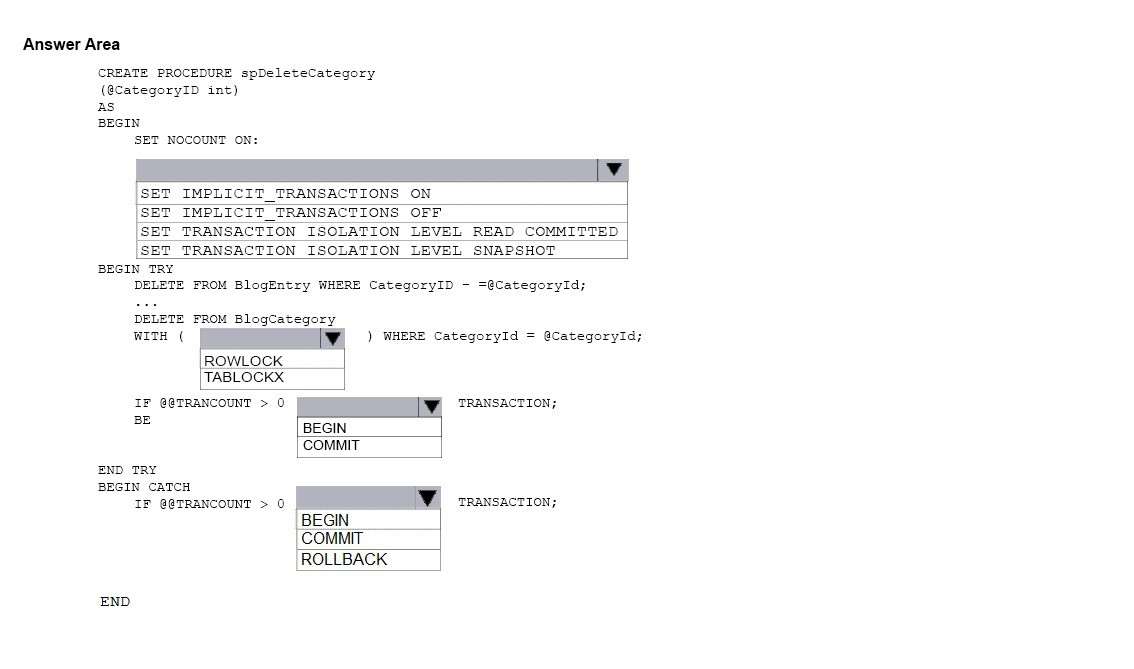
You need to create a stored procedure named spDeleteCategory to delete records in the database. The stored
procedure must meet the following requirments:
1. Delete records in both the BlogEntry and BlogCategory tables where CategoryId equals parameter
@CategoryId.
2. Avoid locking the entire table when deleting records from the BlogCategory table.
3. If an error occurs during a delete operation on either table, all changes must be rolled back, otherwise all
changes should be committed.
How should you complete the procedure? To answer, select the appropriate Transact-SQL segments in the
answer area.
Hot Area:
What are the consistency and concurrency implications o…
DRAG DROP
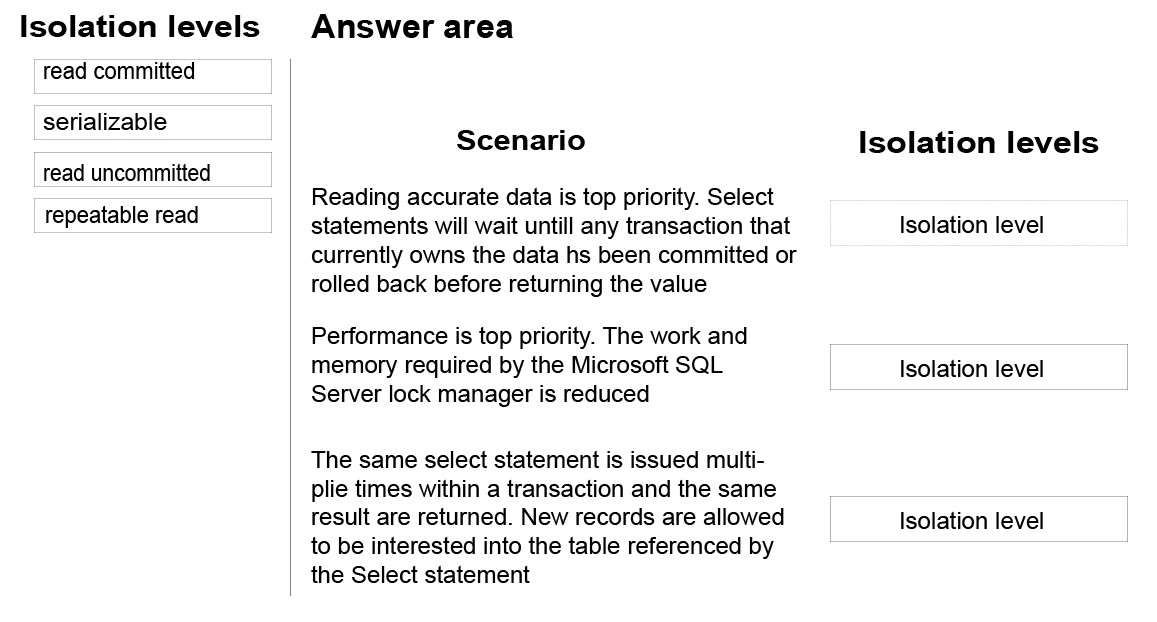
You are analyzing the performance of a database environment.
Applications that access the database are experiencing locks that are held for a large amount of time. You are
experiencing isolation phenomena such as dirty, nonrepeatable and phantom reads.
You need to identify the impact of specific transaction isolation levels on the concurrency and consistency of
data.
What are the consistency and concurrency implications of each transaction isolation level? To answer, drag the
appropriate isolation levels to the correct locations. Each isolation level may be used once, more than once, or
not at all. You may need to drag the split bar between panes or scroll to view content.
Select and Place:
Which isolation level should you use for each scenario?
DRAG DROP
You are evaluating the performance of a database environment.
You must avoid unnecessary locks and ensure that lost updates do not occur.
You need to choose the transaction isolation level for each data scenario.
Which isolation level should you use for each scenario? To answer, drag the appropriate isolation levels to the
correct scenarios. Each isolation may be used once, more than once, or not at all. You may need to drag the
split bar between panes or scroll to view content.
Select and Place:
Which Transact-SQL statement should you run for each table?
DRAG DROP
You have two database tables. Table1 is a partioned table and Table 2 is a nonpartioned table.
Users report that queries take a long time to complete. You monitor queries by using Microsoft SQL Server
Profiler. You observe lock escalation for Table1 and Table 2.
You need to allow escalation of Table1 locks to the partition level and prevent all lock escalation for Table2.
Which Transact-SQL statement should you run for each table? To answer, drag the appropriate Transact-SQL
statements to the correct tables. Each command may be used once, more than once, or not at all. You may
need to drag the split bar between panes or scroll to view content.
Select and Place:
Which four Transact-SQL segments should you use to deve…
DRAG DROP
You have a database that contains three encrypted store procedures named dbo.Proc1, dbo.Proc2 and
dbo.Proc3. The stored procedures include INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE and BACKUP DATABASE statements.
You have the following requirements:
– You must run all the stored procedures within the same transaction.
– You must automatically start a transaction when stored procedures include DML statements.
– You must not automatically start a transaction when stored procedures include DDL statements.
You need to run all three stored procedures.
Which four Transact-SQL segments should you use to develop the solution? To answer, move the appropriate
Transact-SQL segments to the answer area and arrange then in the correct order.
Select and Place:
How should you modify the stored procedure?
HOTSPOT
You are profiling a frequently used database table named UserEvents. The READ_COMMITED_SNAPSHOT
database option is set to OFF.
In the trace results, you observe that lock escalation occurred for one stored procedure even though the
number of locks in the database did not exceed memory or configuration thresholds. Events details are
provided in the following table:
You need to modify the uspDeleteEvents stored procedure to avoid lock escalation.
How should you modify the stored procedure? To answer, select the appropriate Transact-SQL segments in the
answer area.
Hot Area:
You need to ensure that all deadlocks are recorded in X…
You have a database that is experiencing deadlock issues when users run queries.
You need to ensure that all deadlocks are recorded in XML format.
What should you do?
You need to use Microsoft SQL Server Profiler to determ…
You are developing an application that connects to a database.
The application runs the following jobs:
The READ_COMMITTED_SNAPSHOT database option is set to OFF, and auto-content is set to ON. Within
the stored procedures, no explicit transactions are defined.If JobB starts before JobA, it can finish in seconds. If JobA starts first, JobB takes a long time to complete.
You need to use Microsoft SQL Server Profiler to determine whether the blocking that you observe in JobB is
caused by locks acquired by JobA.
Which trace event class in the Locks event category should you use?
Which programming object should you use for each module?
HOTSPOT
You have a database that contains both disk-based and memory-optimized tables.
You need to create two modules. The modules must meet the requirements described in the following table.
Which programming object should you use for each module? To answer, select the appropriate object types in
the answer area.
Hot Area: