Which four Transact-SQL segments should you use to deve…
DRAG DROP
You have a database that contains three encrypted store procedures named dbo.Proc1, dbo.Proc2 and
dbo.Proc3. The stored procedures include INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE and BACKUP DATABASE statements.
You have the following requirements:
– You must run all the stored procedures within the same transaction.
– You must automatically start a transaction when stored procedures include DML statements.
– You must not automatically start a transaction when stored procedures include DDL statements.
You need to run all three stored procedures.
Which four Transact-SQL segments should you use to develop the solution? To answer, move the appropriate
Transact-SQL segments to the answer area and arrange then in the correct order.
Select and Place:
Which Transact-SQL statement should you run for each table?
DRAG DROP
You have two database tables. Table1 is a partioned table and Table 2 is a nonpartioned table.
Users report that queries take a long time to complete. You monitor queries by using Microsoft SQL Server
Profiler. You observe lock escalation for Table1 and Table 2.
You need to allow escalation of Table1 locks to the partition level and prevent all lock escalation for Table2.
Which Transact-SQL statement should you run for each table? To answer, drag the appropriate Transact-SQL
statements to the correct tables. Each command may be used once, more than once, or not at all. You may
need to drag the split bar between panes or scroll to view content.
Select and Place:
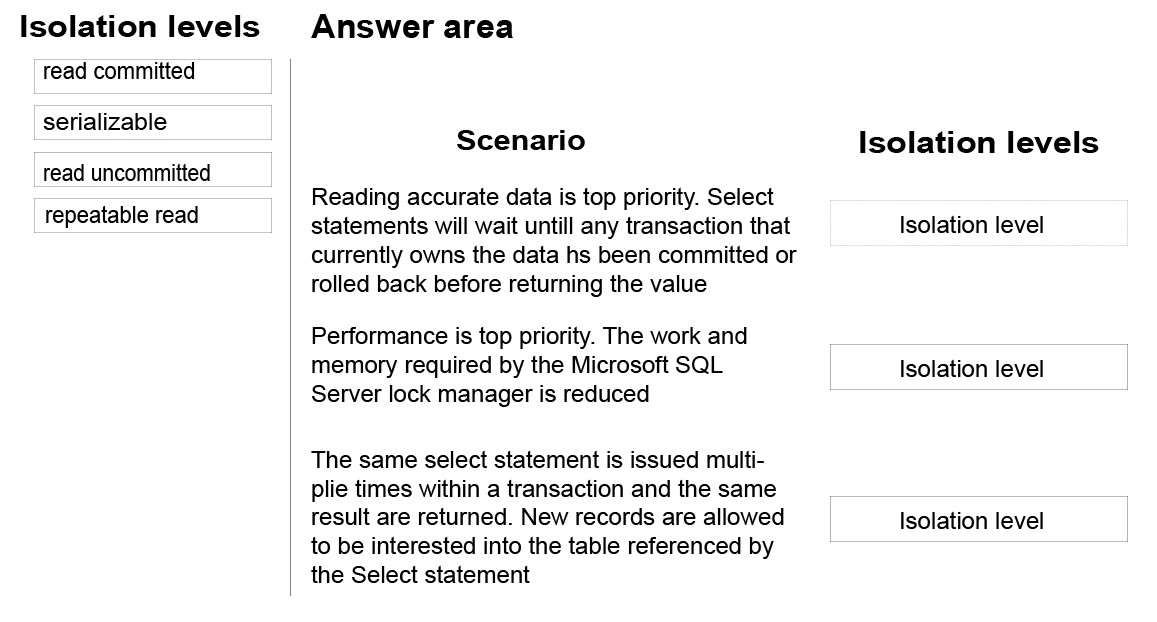
Which isolation level should you use for each scenario?
DRAG DROP
You are evaluating the performance of a database environment.
You must avoid unnecessary locks and ensure that lost updates do not occur.
You need to choose the transaction isolation level for each data scenario.
Which isolation level should you use for each scenario? To answer, drag the appropriate isolation levels to the
correct scenarios. Each isolation may be used once, more than once, or not at all. You may need to drag the
split bar between panes or scroll to view content.
Select and Place:
What are the consistency and concurrency implications o…
DRAG DROP
You are analyzing the performance of a database environment.
Applications that access the database are experiencing locks that are held for a large amount of time. You are
experiencing isolation phenomena such as dirty, nonrepeatable and phantom reads.
You need to identify the impact of specific transaction isolation levels on the concurrency and consistency of
data.
What are the consistency and concurrency implications of each transaction isolation level? To answer, drag the
appropriate isolation levels to the correct locations. Each isolation level may be used once, more than once, or
not at all. You may need to drag the split bar between panes or scroll to view content.
Select and Place:
You need to ensure that all deadlocks are recorded in X…
You have a database that is experiencing deadlock issues when users run queries.
You need to ensure that all deadlocks are recorded in XML format.
What should you do?
You need to use Microsoft SQL Server Profiler to determ…
You are developing an application that connects to a database.
The application runs the following jobs:
The READ_COMMITTED_SNAPSHOT database option is set to OFF, and auto-content is set to ON. Within
the stored procedures, no explicit transactions are defined.If JobB starts before JobA, it can finish in seconds. If JobA starts first, JobB takes a long time to complete.
You need to use Microsoft SQL Server Profiler to determine whether the blocking that you observe in JobB is
caused by locks acquired by JobA.
Which trace event class in the Locks event category should you use?
Which programming object should you use for each module?
HOTSPOT
You have a database that contains both disk-based and memory-optimized tables.
You need to create two modules. The modules must meet the requirements described in the following table.
Which programming object should you use for each module? To answer, select the appropriate object types in
the answer area.
Hot Area:
You need to implement the design changes while minimizi…
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that use the same scenario. For your convenience, the
scenario is repeated in each question. Each question presents a different goal and answer choices, but the text
of the scenario is exactly the same in each question in this series.
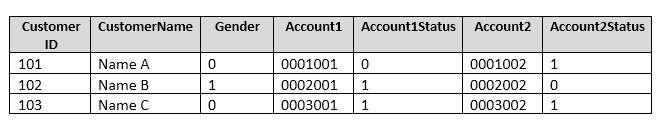
You have a database named DB1 that contains the following tables: Customer, CustomerToAccountBridge,
and CustomerDetails. The three tables are part of the Sales schema. The database also contains a schema
named Website. You create the Customer table by running the following Transact-SQL statement:
The value of the CustomerStatus column is equal to one for active customers. The value of the Account1Status
and Account2Status columns are equal to one for active accounts. The following table displays selected
columns and rows from the Customer table.
You plan to create a view named Website.Customer and a view named Sales.FemaleCustomers.
Website.Customer must meet the following requirements:
1. Allow users access to the CustomerName and CustomerNumber columns for active customers.
2. Allow changes to the columns that the view references. Modified data must be visible through the view.
3. Prevent the view from being published as part of Microsoft SQL Server replication.
Sales.Female.Customers must meet the following requirements:
1. Allow users access to the CustomerName, Address, City, State and PostalCode columns.
2. Prevent changes to the columns that the view references.
3. Only allow updates through the views that adhere to the view filter.
You have the following stored procedures: spDeleteCustAcctRelationship and spUpdateCustomerSummary.
The spUpdateCustomerSummary stored procedure was created by running the following Transacr-SQL
statement:
You run the spUpdateCustomerSummary stored procedure to make changes to customer account summaries.
Other stored procedures call the spDeleteCustAcctRelationship to delete records from the
CustomerToAccountBridge table.
You must update the design of the Customer table to meet the following requirements.
1. You must be able to store up to 50 accounts for each customer.
2. Users must be able to retrieve customer information by supplying an account number.
3. Users must be able to retrieve an account number by supplying customer information.
You need to implement the design changes while minimizing data redundancy.
What should you do?
What is the impact of the stored procedure on the Custo…
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that use the same scenario. For your convenience, the
scenario is repeated in each question. Each question presents a different goal and answer choices, but the text
of the scenario is exactly the same in each question in this series.
You have a database named DB1 that contains the following tables: Customer, CustomerToAccountBridge,
and CustomerDetails. The three tables are part of the Sales schema. The database also contains a schema
named Website. You create the Customer table by running the following Transact-SQL statement:
The value of the CustomerStatus column is equal to one for active customers. The value of the Account1Status
and Account2Status columns are equal to one for active accounts. The following table displays selected
columns and rows from the Customer table.
You plan to create a view named Website.Customer and a view named Sales.FemaleCustomers.
Website.Customer must meet the following requirements:
1. Allow users access to the CustomerName and CustomerNumber columns for active customers.
2. Allow changes to the columns that the view references. Modified data must be visible through the view.
3. Prevent the view from being published as part of Microsoft SQL Server replication.
Sales.Female.Customers must meet the following requirements:
1. Allow users access to the CustomerName, Address, City, State and PostalCode columns.
2. Prevent changes to the columns that the view references.
3. Only allow updates through the views that adhere to the view filter.
You have the following stored procedures: spDeleteCustAcctRelationship and spUpdateCustomerSummary.
The spUpdateCustomerSummary stored procedure was created by running the following Transacr-SQL
statement:
You run the uspUpdateCustomerSummary stored procedure to make changes to customer account
summaries. Other stored procedures call the spDeleteCustAcctRelationship to delete records from the
CustomerToAccountBridge table.
When you start uspUpdateCustomerSummary, there are no active transactions. The procedure fails at the
second update statement due to a CHECK constraint violation on the TotalDepositAccountCount column.
What is the impact of the stored procedure on the CustomerDetails table?
How should you complete the view definition?
DRAG DROP
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that use the same scenario. For your convenience, the
scenario is repeated in each question. Each question presents a different goal and answer choices, but the text
of the scenario is exactly the same in each question in this series.
You have a database named DB1 that contains the following tables: Customer, CustomerToAccountBridge,
and CustomerDetails. The three tables are part of the Sales schema. The database also contains a schema
named Website. You create the Customer table by running the following Transact-SQL statement:
The value of the CustomerStatus column is equal to one for active customers. The value of the Account1Status
and Account2Status columns are equal to one for active accounts. The following table displays selected
columns and rows from the Customer table.
You plan to create a view named Website.Customer and a view named Sales.FemaleCustomers.
Website.Customer must meet the following requirements:
1. Allow users access to the CustomerName and CustomerNumber columns for active customers.
2. Allow changes to the columns that the view references. Modified data must be visible through the view.
3. Prevent the view from being published as part of Microsoft SQL Server replication.
Sales.Female.Customers must meet the following requirements:
1. Allow users access to the CustomerName, Address, City, State and PostalCode columns.
2. Prevent changes to the columns that the view references.
3. Only allow updates through the views that adhere to the view filter.
You have the following stored procedures: spDeleteCustAcctRelationship and spUpdateCustomerSummary.
The spUpdateCustomerSummary stored procedure was created by running the following Transacr-SQL
statement:
You run the spUpdateCustomerSummary stored procedure to make changes to customer account summaries.
Other stored procedures call the spDeleteCustAcctRelationship to delete records from the
CustomerToAccountBridge table.
You need to create Sales.FemaleCustomers.
How should you complete the view definition? To answer, drag the appropriate Transact-SQL segments to the
correct locations. Each Transact_SQL segment may be used once, more than once or not at all. You may need
to drag the split bar between panes or scroll to view content.
Select and Place: