There are several different modes that block ciphers can work in. Which mode does the graphic that follows portray?

A.
Electronic Code Book Mode
B.
Cipher Block Chaining
C.
Output Feedback Mode
D.
Counter Mode
Explanation:
B: Block ciphers have several modes of operation. Each mode specifies how a block cipher will operate. One mode may work better in one type of environment for specific
functionality, whereas another mode may work better in another environment with totally different requirements. Cipher Block Chaining (CBC) does not reveal a pattern, because each
block of text, the key, and the value based on the previous block are processed in the algorithm and applied to the next block of text. This results in more random ciphertext. Ciphertext
is extracted and used from the previous block of text. This provides dependence between the blocks, in a sense chaining them together. This is where the name Cipher Block Chaining
comes from, and it is this chaining effect that hides any patterns.
A is incorrect because Electronic Code Book Mode (ECB) operates like a code book. A 64-bit data block is entered into the algorithm with a key, and a block of ciphertext is
produced. For a given block of plaintext and a given key, the same block of ciphertext is always produced. Not all messages end up in neat and tidy 64-bit blocks, so ECB incorporates
padding to address this problem. ECB is the easiest and fastest mode to use, but as we will see, it has its dangers. In ECB mode, a block of plaintext and a key will always give the
same ciphertext. This means that if the word “balloon” were encrypted and the resulting ciphertext were “hwicssn,” each time it was encrypted using the same key, the same ciphertext
would always be given. This can show evidence of a pattern, enabling an evildoer, with some effort, to discover the pattern and get a step closer to compromising the encryption
process.
C is incorrect because Output Feedback Mode (OFB) is a mode that a block cipher can work in when it needs to emulate a stream, because it encrypts small amounts of data at a
time, but it has a smaller chance of creating and extending errors throughout the full encryption process.
D is incorrect because Counter Mode (CTR) is very similar to OFB mode, but instead of using a randomly unique initialization vector (IV) value to generate the keystream values,
this mode uses an IV counter that increments for each plaintext block that needs to be encrypted.


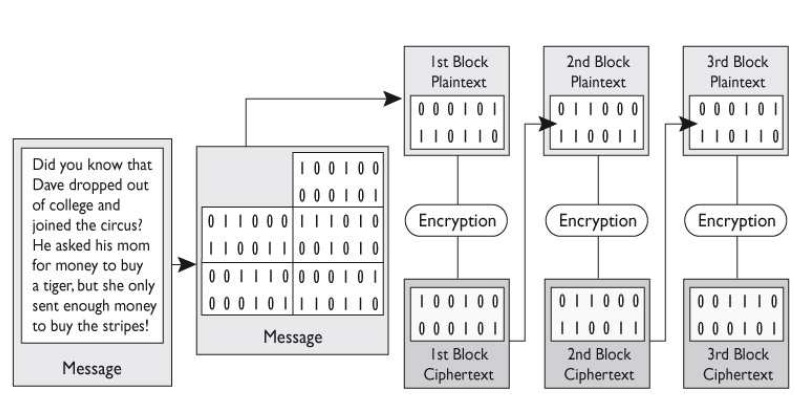
Cipher Block Chaining (CBC) does not reveal a pattern, because each
block of text, the key, and the value based on the previous block are processed in the algorithm and applied to the next block of text. This results in more random ciphertext. Ciphertext is extracted and used from the previous block of text. This provides dependence between the blocks, in a sense chaining them together. This is where the name Cipher Block Chaining comes from, and it is this chaining effect that hides any patterns.
0
0