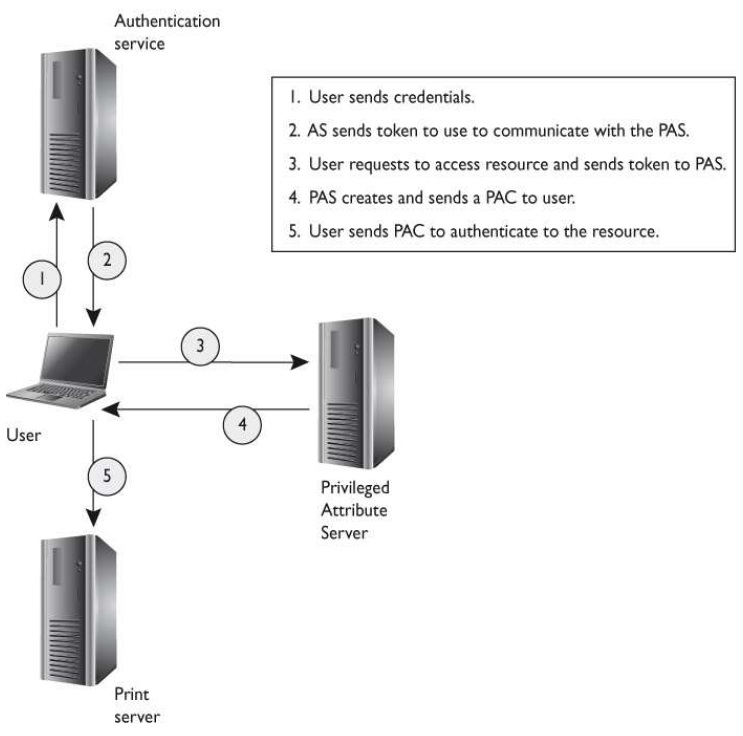
There are several different types of single sign-on protocols and technologies in use today. What type of technology is illustrated in the graphic that follows?

A.
Kerberos
B.
Discretionary access control
C.
SESAME
D.
Mandatory access control
Explanation:
C: The Secure European System for Applications in a Multivendor Environment (SESAME) project has been a single sign-on technology developed to extend Kerberos functionality
and improve upon its weaknesses. SESAME uses symmetric and asymmetric cryptographic techniques to authenticate subjects to network resources. Kerberos uses tickets to
authenticate subjects to objects, whereas SESAME uses Privileged Attribute Certificates (PACs), which contain the subject’s identity, access capabilities for the object, access time
period, and lifetime of the PAC. The PAC is digitally signed so that the object can validate it came from the trusted authentication server, which is referred to as the Privileged Attribute
Server (PAS). The PAS holds a similar role to that of the Key Distribution Center (KDC) within Kerberos. After a user successfully authenticates to the authentication service (AS), he is
presented with a token to give to the PAS. The PAS then creates a PAC for the user to present to the resource he is trying to access.
A is incorrect because Kerberos is an authentication protocol and is based on symmetric key cryptography. Kerberos is an example of a single sign-on system for distributed
environments (as is SESAME) but is the de facto standard for heterogeneous networks today. Kerberos incorporates a wide range of security capabilities, which gives companies
much more flexibility and scalability when they need to provide an encompassing security architecture. It has four elements necessary for enterprise access control: scalability,
transparency, reliability, and security. The differences between these technologies are described more in the previous answer. While SESAME and Kerberos are close in the
functionality they present, SESAME is the technology shown in the graphic.
B is incorrect because discretionary access control (DAC) is an access control model that is built right into an operating system or application, not something that works as a single
sign-on technology. A system that uses discretionary access control (DAC) enables the owner of the resource to specify which subjects can access specific resources. This model is
called discretionary because the control of access is based on the discretion of the owner. Many times department managers, or business unit managers, are the owners of the data
within their specific department. Being the owner, they can specify who should have access and who should not. In a DAC model, access is restricted based on the authorization
granted to the users. This means users are allowed to specify what type of access can occur to the objects they own. The most common implementation of DAC is through ACLs,
which are dictated and set by the owners and enforced by the operating system. This can make a user’s ability to access information dynamic versus the more static role of mandatory
access control (MAC).
D is incorrect because mandatory access control (MAC) is an access control model that is built right into an operating system or application, not something that works as a single
sign-on technology. In a MAC model, users and data owners do not have as much freedom to determine who can access files. The operating system makes the final decision and can
override the users’ wishes. This model is much more structured and strict and is based on a security label system. Users are given a security clearance (secret, top secret, confidential,
and so on), and data is classified in the same way. The clearance and classification data are stored in the security labels, which are bound to the specific subjects and objects. When
the system makes a decision about fulfilling a request to access an object, it is based on the clearance of the subject, the classification of the object, and the security policy of the
system. The rules for how subjects access objects are made by the security officer, configured by the administrator, enforced by the operating system, and supported by security
technologies.