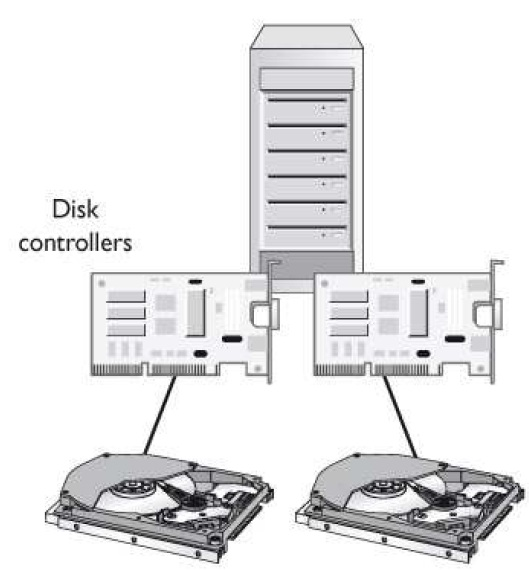
Mirroring of drives is when data is written to two drives at once for redundancy purposes. What similar type of technology is shown in the graphic that follows?

A.
Direct access storage
B.
Disk duplexing
C.
Striping
D.
Massive array of inactive disks
Explanation:
B: Information that is required to always be available should be mirrored or duplexed. In both mirroring (also known as RAID 1) and duplexing, every data write
operation occurs simultaneously or nearly simultaneously in more than one physical place. The distinction between mirroring and duplexing is that with mirroring
the two (or more) physical places where the data is written may be attached to the same controller, leaving the storage still subject to the single point of failure of
the controller itself; in duplexing, two or more controllers are used.
+ A is incorrect because direct success storage is a general term for magnetic disk storage devices, which historically have been used in mainframe and
minicomputer (mid-range computer) environments. A redundant array of independent disks (RAID) is a type of Direct Success Storage Device (DASD).
+ C is incorrect because when data is written across all drives, the technique of striping is used. This activity divides and writes the data over several drives. The
write performance is not affected, but the read performance is increased dramatically because more than one head is retrieving data at the same time. Parity
information is used to rebuild lost or corrupted data. Striping just means data and potentially parity information is written across multiple disks.
+ D is incorrect because in a massive array of inactive disks (MAID), rack-mounted disk arrays have all inactive disks powered down, with only the disk controller
alive. When an application asks for data, the controller powers up the appropriate disk drive(s), transfers the data, and then powers the drive(s) down again. By
powering down infrequently accessed drives, energy consumption is significantly reduced, and the service life of the disk drives may be increased.