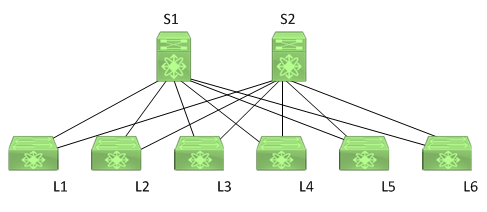
You manage the Cisco FabricPath network in the following exhibit:
A host that is directly connected to L2 sends a unicast packet to a known host that is also directly connected to L2.
Which of the following is true?
A. L2 receives an unknown unicast packet from the sending host.
B. L2 will forward the packet to the multidestination tree.
C. L2 will not perform a lookup on the destination MAC address.
D. L2 will not forward the packet to a spine switch.
Explanation:

L2 will not forward the packet to a spine switch. In this scenario, it is not necessary for L2 to forward the packet to a spine switch, because both the sending host and the receiving host are directly connected to L2. If the destination host in this scenario were connected to a different leaf switch, the known unicast packet would be forwarded from L2 to one of the spine switches and then on to the switch on which the destination host is located.
When L2 receives a known unicast packet, which is unicast packet with a destination address that the switch knows how to reach, that is intended for a host on a different switch the following occurs:
• L2 performs a Media Access Control (MAC) address lookup and located the destination switch.
• L2 looks up the switch ID of the destination switch and chooses a FabricPath core port on which to send the packet.
• L2 encapsulated the packet in a FabricPath header, including its own switch ID in the outer source address (OSA) field and the destination switch’s ID in the outer destination address (ODA) field.
• L2 sends the packet.
By contrast, when L2 receives an unknown unicast packet, the following occurs:
• L2 updates the classic Ethernet MAC table with the sending host’s source Mac address.
• L2 performs a lookup for the destination Mac address of the destination host.
• L2 encapsulates the classic Ethernet frame in a FabricPath header and floods it to the multidestination forwarding tree with L2’s switch ID as the OSA.
Because of the spine-and-leaf configuration of the topology, L2 would flood an unknown unicast packet to its directly connected spine switches, S1 and S2, which would then flood the packet to the other leaf switches. Each leaf switch would then perform a MAC address lookup. The switch that has the destination host in its MAC address table adds the sending host to its own MAC address table. At this point, the packet is sent to the destination host.
Reference:
Cisco Press CCNA Data Center DCICT 200-155 Official Cert Guide, Chapter 1: Data Center Networking, FabricPath Packet Flow Example, pp. 38-40