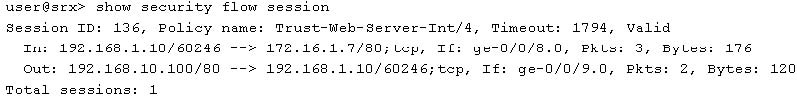
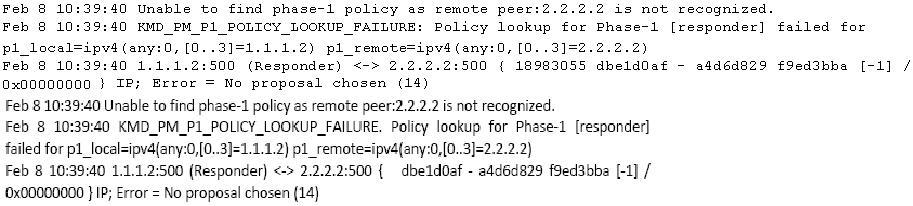
What is causing this behavior?
Click the Exhibit button. — Exhibit – — Exhibit — In the network shown in the exhibit, you
want to forward traffic from the employees to ISP1 and ISP2. You want to forward all Web
traffic to ISP1 and all other traffic to ISP2. However, your configuration is not producing the
expected results. Part of the configuration is shown in the exhibit. When you run the show
route table isp1 command, you do not see the default route listed. What is causing this
behavior?
What is the reason for this behavior?
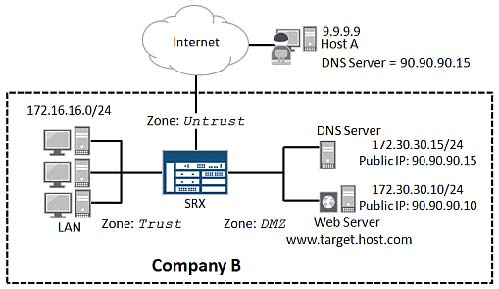
What would cause this behavior on the SRX device in Company B’s network?
Click the Exhibit button. — Exhibit – — Exhibit — Host A cannot resolve the
www.target.host.com Web page when using its configured DNS server. As shown in the
exhibit, Host A’s configured DNS server and the Web server hosting the
www.target.host.com Web page are in the same subnet. You have verified bidirectional
reachability between Host A and the Web server hosting the Web page. What would cause
this behavior on the SRX device in Company B’s network?
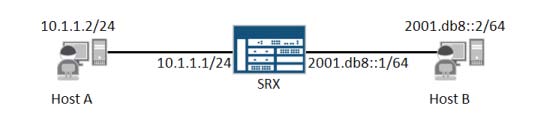
What are three configuration requirements?
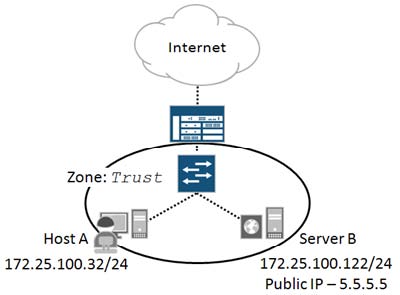
which two configuration tasks will allow Host A to telnet to the public IP address associated with Server B?
Which configuration will accomplish this task?
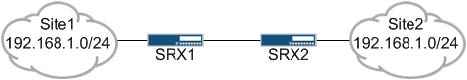
Click the Exhibit button. — Exhibit – — Exhibit — You must configure two SRX devices to
enable bidirectional communications between the two networks shown in the exhibit. You
have been allocated the 172.16.1.0/24 and 172.16.2.0/24 networks to use for this purpose.
Which configuration will accomplish this task?
what are two results?
How do you accomplish this goal?
Click the Exhibit button. — Exhibit — — Exhibit — You are migrating from one external
address block to a different external address block. You want to enable a smooth transition
to the new address block. You temporarily want to allow external users to contact the Web
server using both the existing external address as well as the new external address
192.168.1.1. How do you accomplish this goal?