There are several different types of important architectures within public key infrastructures. Which architecture does the graphic that follows represent?

A.
Cross-certification
B.
Cross-revocation list
C.
Online Certificate Status Protocol
D.
Registration authority
Explanation:
A: When independent PKIs need to interconnect to allow for secure communication to take place (either between departments or different companies), there must be a way for the
two root CAs to trust each other. The two CAs do not have a CA above them they can both trust, so they must carry out cross-certification. A cross-certification is the process
undertaken by CAs to establish a trust relationship in which they rely upon each other’s digital certificates and public keys as if they had issued them themselves. When this is set up, a
CA for one company can validate digital certificates from the other company and vice versa.
B is incorrect because a cross-revocation list (CRL) contains all of the revoked certifications within a PKI. The CA is responsible for creating and handing out certificates, maintaining
them, and revoking them if necessary. Revocation is handled by the CA, and the revoked certificate information is stored on a CRL. This is a list of every certificate that has been
revoked. This list is maintained and updated periodically. A certificate may be revoked because the key holder’s private key was compromised or because the CA discovered the
certificate was issued to the wrong person. An analogy for the use of a CRL is how a driver’s license is used by a police officer. If an officer pulls over Sean for speeding, the officer will
ask to see Sean’s license. The officer will then run a check on the license to find out if Sean is wanted for any other infractions of the law and to verify the license has not expired. The
same thing happens when a person compares a certificate to a CRL. If the certificate became invalid for some reason, the CRL is the mechanism for the CA to let others know this
information.
C is incorrect because the Online Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP) carries out real-time validation of a certificate and reports back to the user whether the certificate is valid,
invalid, or unknown. When using just a CRL, the user’s browser must either check a central CRL to find out if the certification has been revoked or continually push out CRL values to
the clients to ensure they have an updated CRL. If OCSP is implemented, it does this work automatically in the background. OCSP checks the CRL that is maintained by the CA. So
the CRL is still being used, but now we have a protocol developed specifically to check the CRL during a certificate validation process.
D is incorrect because the registration authority (RA) performs the certification registration duties. The RA establishes and confirms the identity of an individual and initiates the
certification process with a CA on behalf of an end user. The RA cannot issue certificates but can act as a broker between the user and the CA. When users need new certificates, they
make requests to the RA, and the RA verifies all necessary identification information before allowing a request to go to the CA.


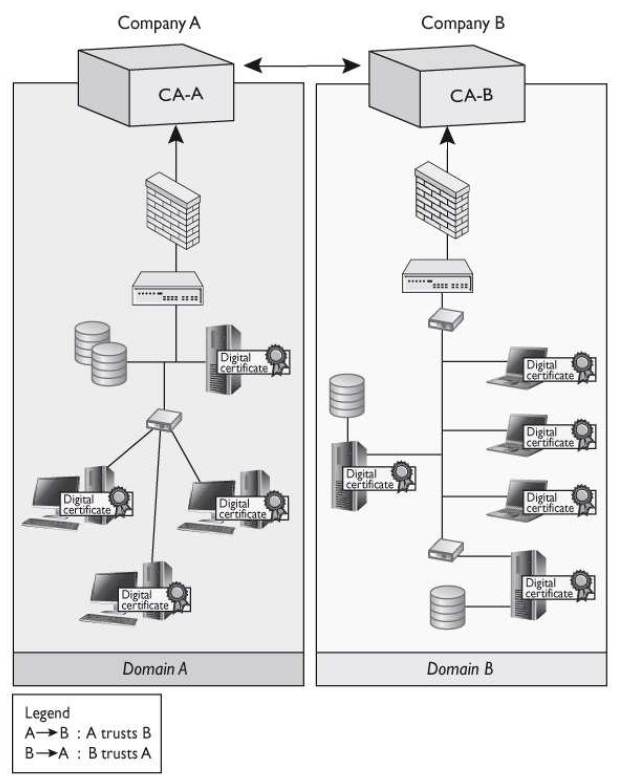
When independent PKIs need to interconnect to allow for secure communication to take place (either between departments or different companies), there must be a way for the two root CAs to trust each other. The two CAs do not have a CA above them they can both trust, so they must carry out cross-certification. A cross-certification is the process undertaken by CAs to establish a trust relationship in which they rely upon each other’s digital certificates and public keys as if they had issued them themselves. When this is set up, a CA for one company can validate digital certificates from the other company and vice versa.
B is incorrect because a cross-revocation list (CRL) contains all of the revoked certifications within a PKI. The CA is responsible for creating and handing out certificates, maintaining them, and revoking them if necessary.
0
0
Online Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP) carries out real-time validation of a certificate and reports back to the user whether the certificate is valid,
invalid, or unknown.
Registration authority (RA) performs the certification registration duties. The RA establishes and confirms the identity of an individual and initiates the
certification process with a CA on behalf of an end user.
0
0